UK researchers cure man who had COVID for 411 days
Accepted manuscripts are PDF versions of the author’s final manuscript, as accepted for publication by the journal but prior to copyediting or typesetting. They can be cited using the author, article title, journal title, year of online publication, and DOI. They will be replaced by the final typeset articles, which may therefore contain changes. The DOI will remain the same throughout.
© The Author 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted reuse, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
© The Author 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Frontiers | SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody trajectories in mothers and infants over two months following maternal infectionInfants exposed to caregivers infected with SARS-CoV-2 may have heightened infection risks relative to older children due to their more intensive care and feeding needs, and may experience more severe infection due to their less developed immune systems. However, there has been limited research on COVID-19 outcomes in exposed infants beyond the neonatal period. Between June 2020 – March 2021, we conducted interviews and collected capillary dried blood from SARS-CoV-2 infected mothers and their infants (aged 1-36 months) for up to two months following maternal infection onset (COVID+ group, 87% breastfeeding, n dyads=46 dyads). Comparative data were also collected from breastfeeding mothers with no known SARS-CoV-2 infection or exposures (breastfeeding control group, n dyads=26), and mothers who tested SARS-CoV-2 negative after experiencing symptoms or close contact exposure (COVID- group, n dyads=11, 73% breastfeeding). Dried blood samples were assayed for anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG and IgA positivity and anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 + S2 IgG concentrations. Within the COVID+ group, the mean probability of seropositivity among infant samples was significantly lower than that of corresponding maternal samples (IgG 0.54 vs. 0.87; IgA 0.33 vs. 0.85), with likelihood of infant infection positively associated with the number of maternal symptoms and other household infections reported. COVID+ mothers reported a lower incidence of COVID-19 symptoms among their infants as compared to themselves and other household adults, and infants had similar PCR positivity rates as other household children. No samples returned by COVID- mothers or their infants tested antibody positive. Among the breastfeeding control group, 44% of mothers but none of their infants tested antibody positive in at least one sample. Results support previous research demonstrating minimal risks to infants following maternal COVID-19 infection, including for breastfeeding infants.
Frontiers | SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody trajectories in mothers and infants over two months following maternal infectionInfants exposed to caregivers infected with SARS-CoV-2 may have heightened infection risks relative to older children due to their more intensive care and feeding needs, and may experience more severe infection due to their less developed immune systems. However, there has been limited research on COVID-19 outcomes in exposed infants beyond the neonatal period. Between June 2020 – March 2021, we conducted interviews and collected capillary dried blood from SARS-CoV-2 infected mothers and their infants (aged 1-36 months) for up to two months following maternal infection onset (COVID+ group, 87% breastfeeding, n dyads=46 dyads). Comparative data were also collected from breastfeeding mothers with no known SARS-CoV-2 infection or exposures (breastfeeding control group, n dyads=26), and mothers who tested SARS-CoV-2 negative after experiencing symptoms or close contact exposure (COVID- group, n dyads=11, 73% breastfeeding). Dried blood samples were assayed for anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG and IgA positivity and anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 + S2 IgG concentrations. Within the COVID+ group, the mean probability of seropositivity among infant samples was significantly lower than that of corresponding maternal samples (IgG 0.54 vs. 0.87; IgA 0.33 vs. 0.85), with likelihood of infant infection positively associated with the number of maternal symptoms and other household infections reported. COVID+ mothers reported a lower incidence of COVID-19 symptoms among their infants as compared to themselves and other household adults, and infants had similar PCR positivity rates as other household children. No samples returned by COVID- mothers or their infants tested antibody positive. Among the breastfeeding control group, 44% of mothers but none of their infants tested antibody positive in at least one sample. Results support previous research demonstrating minimal risks to infants following maternal COVID-19 infection, including for breastfeeding infants.
Lire la suite »
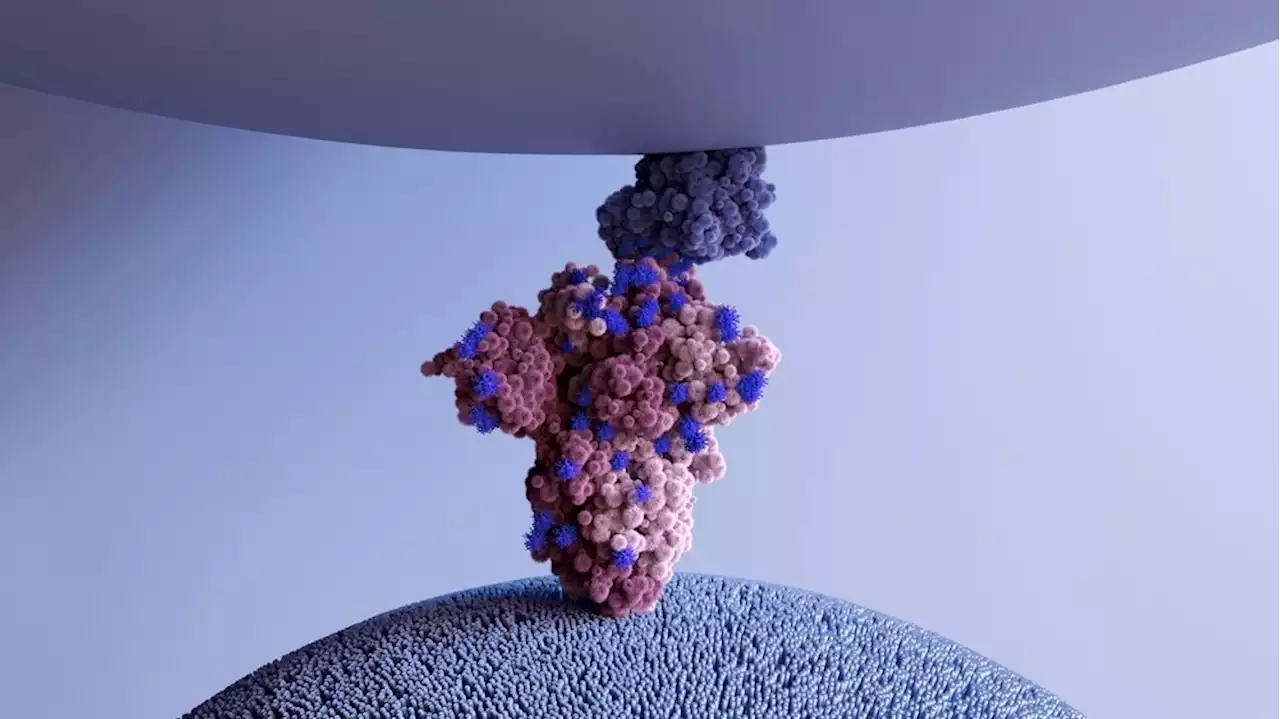 Vimentin is an important co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 infectionVimentin is an important co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 infection Receptor SARSCoV2 Coronavirus Disease COVID ACE2 Vimentin iScience_CP IHU_Marseille univamu
Vimentin is an important co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 infectionVimentin is an important co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 infection Receptor SARSCoV2 Coronavirus Disease COVID ACE2 Vimentin iScience_CP IHU_Marseille univamu
Lire la suite »
 Bivalent mRNA booster broadens humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariantsResearchers at Emory University, Stanford University, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases evaluated whether bivalent coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) boosters conferred protection against new Omicron subvariants.
Bivalent mRNA booster broadens humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariantsResearchers at Emory University, Stanford University, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases evaluated whether bivalent coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) boosters conferred protection against new Omicron subvariants.
Lire la suite »
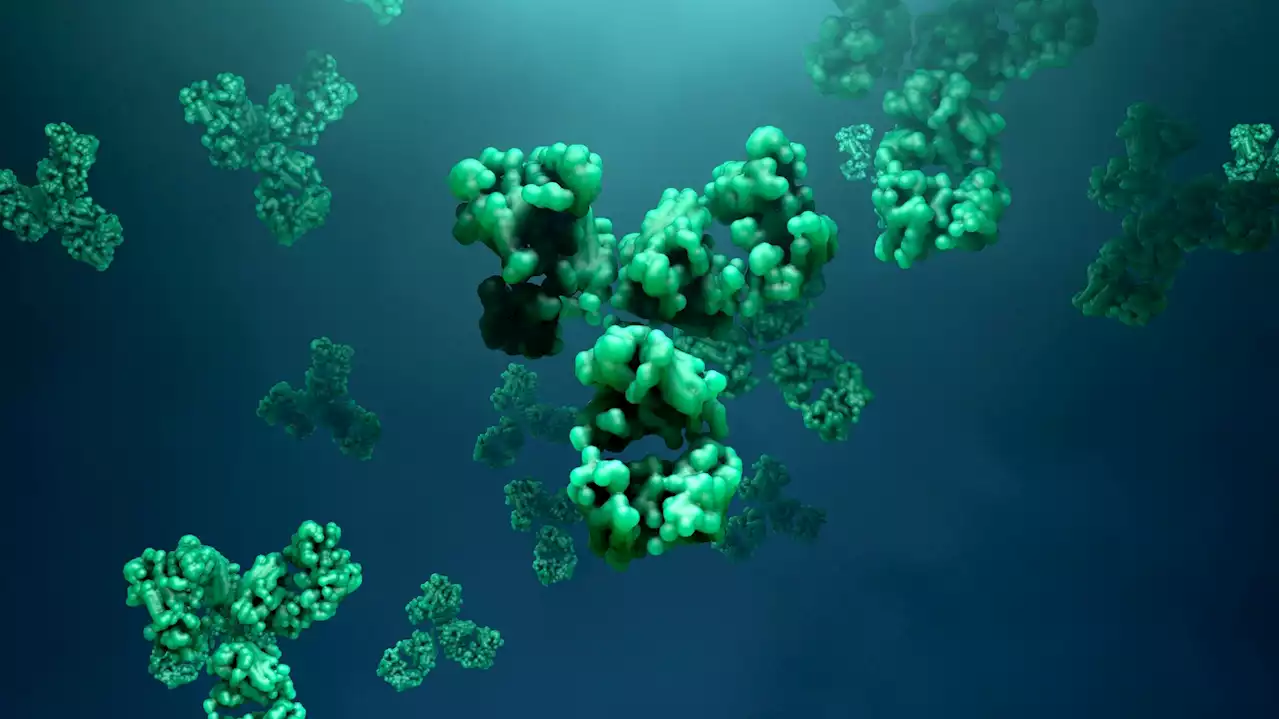 Scientists identify a broadly neutralizing antibody against all dominant SARS-CoV-2 variantsScientists identify a broadly neutralizing antibody against all dominant SARS-CoV-2 variants Antibody SARSCoV2 Coronavirus Disease COVID biorxivpreprint WeillCornell UWMadison scrippsresearch UChicago IcahnMountSinai seattlechildren
Scientists identify a broadly neutralizing antibody against all dominant SARS-CoV-2 variantsScientists identify a broadly neutralizing antibody against all dominant SARS-CoV-2 variants Antibody SARSCoV2 Coronavirus Disease COVID biorxivpreprint WeillCornell UWMadison scrippsresearch UChicago IcahnMountSinai seattlechildren
Lire la suite »
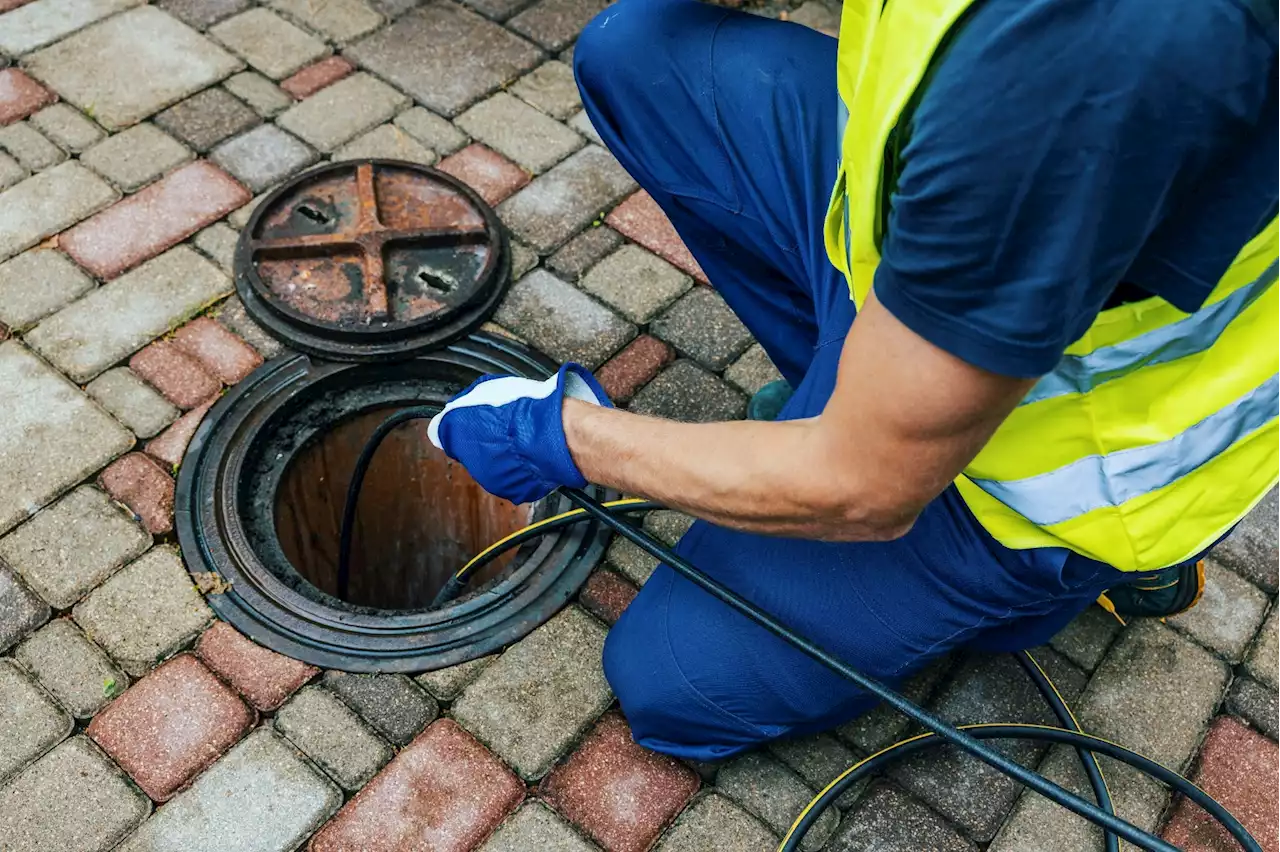 Scientists identify a cryptic SARS-CoV-2 lineage in wastewaterIn a recent study posted to the medRxiv* preprint server, researchers in the United States investigated the source of an enigmatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant of concern (VOC)-like spike (S) protein strain detected in wastewater but not in clinical samples.
Scientists identify a cryptic SARS-CoV-2 lineage in wastewaterIn a recent study posted to the medRxiv* preprint server, researchers in the United States investigated the source of an enigmatic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Omicron variant of concern (VOC)-like spike (S) protein strain detected in wastewater but not in clinical samples.
Lire la suite »
