A study published in BMCMusculoSkeletDisord finds that stress, depressive and anxiety symptoms are associated with poorer health outcomes in patients with neck pain with or without radiculopathy.
Assessed psychosocial factors or mental health symptoms as an exposure. Studies must have investigated one or more psychosocial or mental health symptoms . Psychosocial factors may have included: cognitive , affective , behavioural , vocational or interpersonal processes []. Mental health symptoms and conditions such as depressive symptoms, clinical depression, anxiety, perceived stress, personality, psychotic, traumatic and eating disorders were also considered.
No restriction on publication date was applied. Studies were excluded if they were animal or cadaveric studies, commentaries, editorials, single case studies, reports or laboratory data, books or book chapters, letters, conference posters or proceedings or study protocols.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Spatiotemporal overlapping of dengue, chikungunya, and malaria infections in children in Kenya - BMC Infectious DiseasesMalaria, chikungunya virus (CHIKV), and dengue virus (DENV) are endemic causes of fever among children in Kenya. The risks of infection are multifactorial and may be influenced by built and social environments. The high resolution overlapping of these diseases and factors affecting their spatial heterogeneity has not been investigated in Kenya. From 2014-2018, we prospectively followed a cohort of children from four communities in both coastal and western Kenya. Overall, 9.8% were CHIKV seropositive, 5.5% were DENV seropositive, and 39.1% were malaria positive (3521 children tested). The spatial analysis identified hot-spots for all three diseases in each site and in multiple years. The results of the model showed that the risk of exposure was linked to demographics with common factors for the three diseases including the presence of litter, crowded households, and higher wealth in these communities. These insights are of high importance to improve surveillance and targeted control of mosquito-borne diseases in Kenya.
Spatiotemporal overlapping of dengue, chikungunya, and malaria infections in children in Kenya - BMC Infectious DiseasesMalaria, chikungunya virus (CHIKV), and dengue virus (DENV) are endemic causes of fever among children in Kenya. The risks of infection are multifactorial and may be influenced by built and social environments. The high resolution overlapping of these diseases and factors affecting their spatial heterogeneity has not been investigated in Kenya. From 2014-2018, we prospectively followed a cohort of children from four communities in both coastal and western Kenya. Overall, 9.8% were CHIKV seropositive, 5.5% were DENV seropositive, and 39.1% were malaria positive (3521 children tested). The spatial analysis identified hot-spots for all three diseases in each site and in multiple years. The results of the model showed that the risk of exposure was linked to demographics with common factors for the three diseases including the presence of litter, crowded households, and higher wealth in these communities. These insights are of high importance to improve surveillance and targeted control of mosquito-borne diseases in Kenya.
Lire la suite »
 High prevalence of metabolic diseases, liver steatosis and fibrosis among Chinese psychiatric patients - BMC PsychiatryBackground We aimed to investigate the differences of metabolic disorders between the general population and psychiatric patients, with an emphasis on the prevalence and influencing factors of liver fibrosis in psychiatric patients. Methods A total of 734 psychiatric patients and 734 general population matched for age, sex, and BMI were enrolled from Shanghai, China. All participants underwent blood pressure, glucose, lipid profile measurements, and anthropometric parameters including body weight, height and waist circumference. FibroScan examinations were also performed on psychiatric patients. Liver steatosis and fibrosis were diagnosed by controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) and liver stiffness measurement (LSM) by professional staff. Results Compared with the general population, psychiatric patients revealed significantly higher burden of metabolic disorders. The overall prevalence of liver steatosis (CAP ≥ 233 dB/m) and fibrosis (LSM ≥ 7.0 kPa) was 48.7% and 15.5% in psychiatric patients. Psychiatric patients with liver steatosis or fibrosis showed worse metabolic profile. Meanwhile, the prevalence of liver fibrosis was also significantly higher in patients with overweight, central obesity, diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and liver steatosis. In logistic regression analyses, age, BMI and visceral adiposity index were independent risk factors for liver fibrosis in psychiatric patients. Additionally, antipsychotic medication was suggested to be associated with an increased risk of liver fibrosis in psychiatric patients with liver steatosis. Conclusions Prevalence of liver steatosis and fibrosis is high in Chinese psychiatric patients. Those with antipsychotic polypharmacy and obesity are at high risk, and may benefit from early liver assessment in preventing fibrosis progression.
High prevalence of metabolic diseases, liver steatosis and fibrosis among Chinese psychiatric patients - BMC PsychiatryBackground We aimed to investigate the differences of metabolic disorders between the general population and psychiatric patients, with an emphasis on the prevalence and influencing factors of liver fibrosis in psychiatric patients. Methods A total of 734 psychiatric patients and 734 general population matched for age, sex, and BMI were enrolled from Shanghai, China. All participants underwent blood pressure, glucose, lipid profile measurements, and anthropometric parameters including body weight, height and waist circumference. FibroScan examinations were also performed on psychiatric patients. Liver steatosis and fibrosis were diagnosed by controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) and liver stiffness measurement (LSM) by professional staff. Results Compared with the general population, psychiatric patients revealed significantly higher burden of metabolic disorders. The overall prevalence of liver steatosis (CAP ≥ 233 dB/m) and fibrosis (LSM ≥ 7.0 kPa) was 48.7% and 15.5% in psychiatric patients. Psychiatric patients with liver steatosis or fibrosis showed worse metabolic profile. Meanwhile, the prevalence of liver fibrosis was also significantly higher in patients with overweight, central obesity, diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and liver steatosis. In logistic regression analyses, age, BMI and visceral adiposity index were independent risk factors for liver fibrosis in psychiatric patients. Additionally, antipsychotic medication was suggested to be associated with an increased risk of liver fibrosis in psychiatric patients with liver steatosis. Conclusions Prevalence of liver steatosis and fibrosis is high in Chinese psychiatric patients. Those with antipsychotic polypharmacy and obesity are at high risk, and may benefit from early liver assessment in preventing fibrosis progression.
Lire la suite »
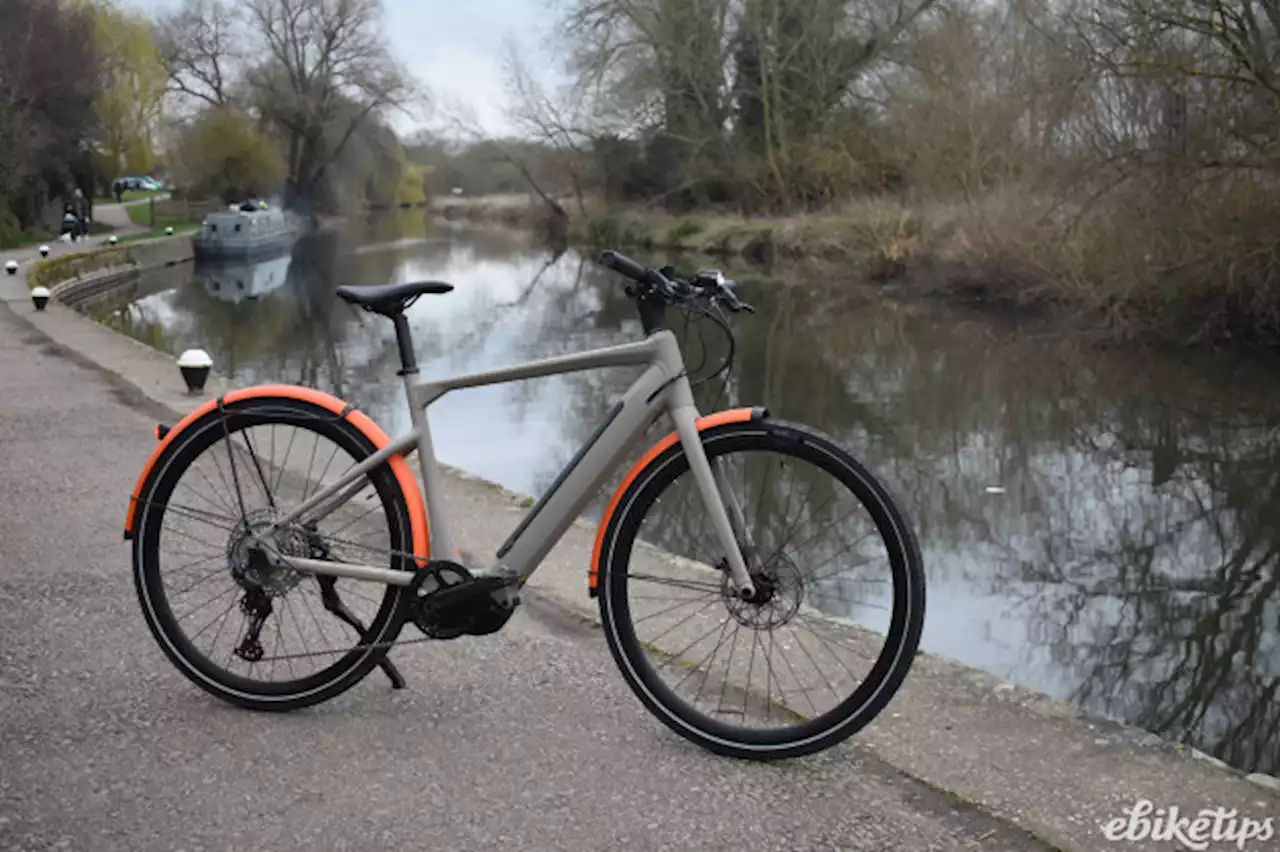 BMC 257 AMP AL TWOSwitzerland's BMC (Bicycle Manufacturing Company) are based in Switzerland and naturally look to bring the Swiss reputation for precision engineering and quality to the world of e-bikes. In this case that means their 257 AMP AL Two e-bike, an extremely stylish looking commuter that boasts a mouth-watering combinaton of a powerful Bosch mid-drive motor, sizeable battery, powerful lights, superstrong mudguards with integrated rear rack and a sophisticated Kiox display.
BMC 257 AMP AL TWOSwitzerland's BMC (Bicycle Manufacturing Company) are based in Switzerland and naturally look to bring the Swiss reputation for precision engineering and quality to the world of e-bikes. In this case that means their 257 AMP AL Two e-bike, an extremely stylish looking commuter that boasts a mouth-watering combinaton of a powerful Bosch mid-drive motor, sizeable battery, powerful lights, superstrong mudguards with integrated rear rack and a sophisticated Kiox display.
Lire la suite »
 Pregnancy-related sensory deficits might impair foraging in echolocating bats - BMC BiologyBackground Reproduction entails substantial demands throughout its distinct stages. The mammalian gestation period imposes various energetic costs and movement deficits, but its effects on the sensory system are poorly understood. Bats rely heavily on active sensing, using echolocation to forage in complete darkness, or when lighting is uncertain. We examined the effects of pregnancy on bat echolocation. Results We show that pregnant Kuhl’s pipistrelles (Pipistrellus kuhlii) altered their echolocation and flight behavior. Specifically, pregnant bats emitted longer echolocation signals at an ~ 15% lower rate, while flying more slowly and at a lower altitude compared to post-lactating females. A sensorimotor foraging model suggests that these changes could lead to an ~ 15% reduction in hunting performance during pregnancy. Conclusions Sensory deficits related to pregnancy could impair foraging in echolocating bats. Our study demonstrates an additional cost of reproduction of possible relevance to other sensory modalities and organisms.
Pregnancy-related sensory deficits might impair foraging in echolocating bats - BMC BiologyBackground Reproduction entails substantial demands throughout its distinct stages. The mammalian gestation period imposes various energetic costs and movement deficits, but its effects on the sensory system are poorly understood. Bats rely heavily on active sensing, using echolocation to forage in complete darkness, or when lighting is uncertain. We examined the effects of pregnancy on bat echolocation. Results We show that pregnant Kuhl’s pipistrelles (Pipistrellus kuhlii) altered their echolocation and flight behavior. Specifically, pregnant bats emitted longer echolocation signals at an ~ 15% lower rate, while flying more slowly and at a lower altitude compared to post-lactating females. A sensorimotor foraging model suggests that these changes could lead to an ~ 15% reduction in hunting performance during pregnancy. Conclusions Sensory deficits related to pregnancy could impair foraging in echolocating bats. Our study demonstrates an additional cost of reproduction of possible relevance to other sensory modalities and organisms.
Lire la suite »
 Association between epicardial adipose tissue and incident heart failure mediating by alteration of natriuretic peptide and myocardial strain - BMC MedicineBackground Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) has been suggested to exert deleterious effects on myocardium and cardiovascular disease (CVD) consequence. We evaluated the associations of EAT thickness with adverse outcomes and its potential mediators in the community. Methods Participants without heart failure (HF) who had undergone cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) to measure EAT thickness over the right ventricular free wall from the Framingham Heart Study were included. The correlation of EAT thickness with 85 circulating biomarkers and cardiometric parameters was assessed in linear regression models. The occurrence of HF, atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease (CHD), and other adverse events was tracked since CMR was implemented. Their associations with EAT thickness and the mediators were evaluated using Cox regression and causal mediation analysis. Results Of 1554 participants, 53.0% were females. Mean age, body mass index, and EAT thickness were 63.3 years, 28.1 kg/m2, and 9.8 mm, respectively. After fully adjusting, EAT thickness positively correlated with CRP, LEP, GDF15, MMP8, MMP9, ORM1, ANGPTL3, and SERPINE1 and negatively correlated with N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), IGFBP1, IGFBP2, AGER, CNTN1, and MCAM. Increasing EAT thickness was associated with smaller left ventricular end-diastolic dimension, thicker left ventricular wall thickness, and worse global longitudinal strain (GLS). During a median follow-up of 12.7 years, 101 incident HF occurred. Per 1-standard deviation increment of EAT thickness was associated with a higher risk of HF (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.43, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.19–1.72, P | 0.001) and the composite outcome consisting of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, HF, and death from CVD (adjusted HR [95% CI], 1.23 [1.07–1.40], P = 0.003). Mediation effect in the association between thicker EAT and higher risk of HF was observed with NT-proBNP (HR [95% CI], 0.95 [0.92–0.98], P = 0.011) and GLS
Association between epicardial adipose tissue and incident heart failure mediating by alteration of natriuretic peptide and myocardial strain - BMC MedicineBackground Epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) has been suggested to exert deleterious effects on myocardium and cardiovascular disease (CVD) consequence. We evaluated the associations of EAT thickness with adverse outcomes and its potential mediators in the community. Methods Participants without heart failure (HF) who had undergone cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) to measure EAT thickness over the right ventricular free wall from the Framingham Heart Study were included. The correlation of EAT thickness with 85 circulating biomarkers and cardiometric parameters was assessed in linear regression models. The occurrence of HF, atrial fibrillation, coronary heart disease (CHD), and other adverse events was tracked since CMR was implemented. Their associations with EAT thickness and the mediators were evaluated using Cox regression and causal mediation analysis. Results Of 1554 participants, 53.0% were females. Mean age, body mass index, and EAT thickness were 63.3 years, 28.1 kg/m2, and 9.8 mm, respectively. After fully adjusting, EAT thickness positively correlated with CRP, LEP, GDF15, MMP8, MMP9, ORM1, ANGPTL3, and SERPINE1 and negatively correlated with N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), IGFBP1, IGFBP2, AGER, CNTN1, and MCAM. Increasing EAT thickness was associated with smaller left ventricular end-diastolic dimension, thicker left ventricular wall thickness, and worse global longitudinal strain (GLS). During a median follow-up of 12.7 years, 101 incident HF occurred. Per 1-standard deviation increment of EAT thickness was associated with a higher risk of HF (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.43, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.19–1.72, P | 0.001) and the composite outcome consisting of myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, HF, and death from CVD (adjusted HR [95% CI], 1.23 [1.07–1.40], P = 0.003). Mediation effect in the association between thicker EAT and higher risk of HF was observed with NT-proBNP (HR [95% CI], 0.95 [0.92–0.98], P = 0.011) and GLS
Lire la suite »
 Non-invasive measurements of respiration and heart rate across wildlife species using Eulerian Video Magnification of infrared thermal imagery - BMC BiologyBackground An animal’s metabolic rate, or energetic expenditure, both impacts and is impacted by interactions with its environment. However, techniques for obtaining measurements of metabolic rate are invasive, logistically difficult, and costly. Red–green–blue (RGB) imaging tools have been used in humans and select domestic mammals to accurately measure heart and respiration rate, as proxies of metabolic rate. The purpose of this study was to investigate if infrared thermography (IRT) coupled with Eulerian video magnification (EVM) would extend the applicability of imaging tools towards measuring vital rates in exotic wildlife species with different physical attributes. Results We collected IRT and RGB video of 52 total species (39 mammalian, 7 avian, 6 reptilian) from 36 taxonomic families at zoological institutions and used EVM to amplify subtle changes in temperature associated with blood flow for respiration and heart rate measurements. IRT-derived respiration and heart rates were compared to ‘true’ measurements determined simultaneously by expansion of the ribcage/nostrils and stethoscope readings, respectively. Sufficient temporal signals were extracted for measures of respiration rate in 36 species (85% success in mammals; 50% success in birds; 100% success in reptiles) and heart rate in 24 species (67% success in mammals; 33% success in birds; 0% success in reptiles) using IRT-EVM. Infrared-derived measurements were obtained with high accuracy (respiration rate, mean absolute error: 1.9 breaths per minute, average percent error: 4.4%; heart rate, mean absolute error: 2.6 beats per minute, average percent error: 1.3%). Thick integument and animal movement most significantly hindered successful validation. Conclusion The combination of IRT with EVM analysis provides a non-invasive method to assess individual animal health in zoos, with great potential to monitor wildlife metabolic indices in situ.
Non-invasive measurements of respiration and heart rate across wildlife species using Eulerian Video Magnification of infrared thermal imagery - BMC BiologyBackground An animal’s metabolic rate, or energetic expenditure, both impacts and is impacted by interactions with its environment. However, techniques for obtaining measurements of metabolic rate are invasive, logistically difficult, and costly. Red–green–blue (RGB) imaging tools have been used in humans and select domestic mammals to accurately measure heart and respiration rate, as proxies of metabolic rate. The purpose of this study was to investigate if infrared thermography (IRT) coupled with Eulerian video magnification (EVM) would extend the applicability of imaging tools towards measuring vital rates in exotic wildlife species with different physical attributes. Results We collected IRT and RGB video of 52 total species (39 mammalian, 7 avian, 6 reptilian) from 36 taxonomic families at zoological institutions and used EVM to amplify subtle changes in temperature associated with blood flow for respiration and heart rate measurements. IRT-derived respiration and heart rates were compared to ‘true’ measurements determined simultaneously by expansion of the ribcage/nostrils and stethoscope readings, respectively. Sufficient temporal signals were extracted for measures of respiration rate in 36 species (85% success in mammals; 50% success in birds; 100% success in reptiles) and heart rate in 24 species (67% success in mammals; 33% success in birds; 0% success in reptiles) using IRT-EVM. Infrared-derived measurements were obtained with high accuracy (respiration rate, mean absolute error: 1.9 breaths per minute, average percent error: 4.4%; heart rate, mean absolute error: 2.6 beats per minute, average percent error: 1.3%). Thick integument and animal movement most significantly hindered successful validation. Conclusion The combination of IRT with EVM analysis provides a non-invasive method to assess individual animal health in zoos, with great potential to monitor wildlife metabolic indices in situ.
Lire la suite »
