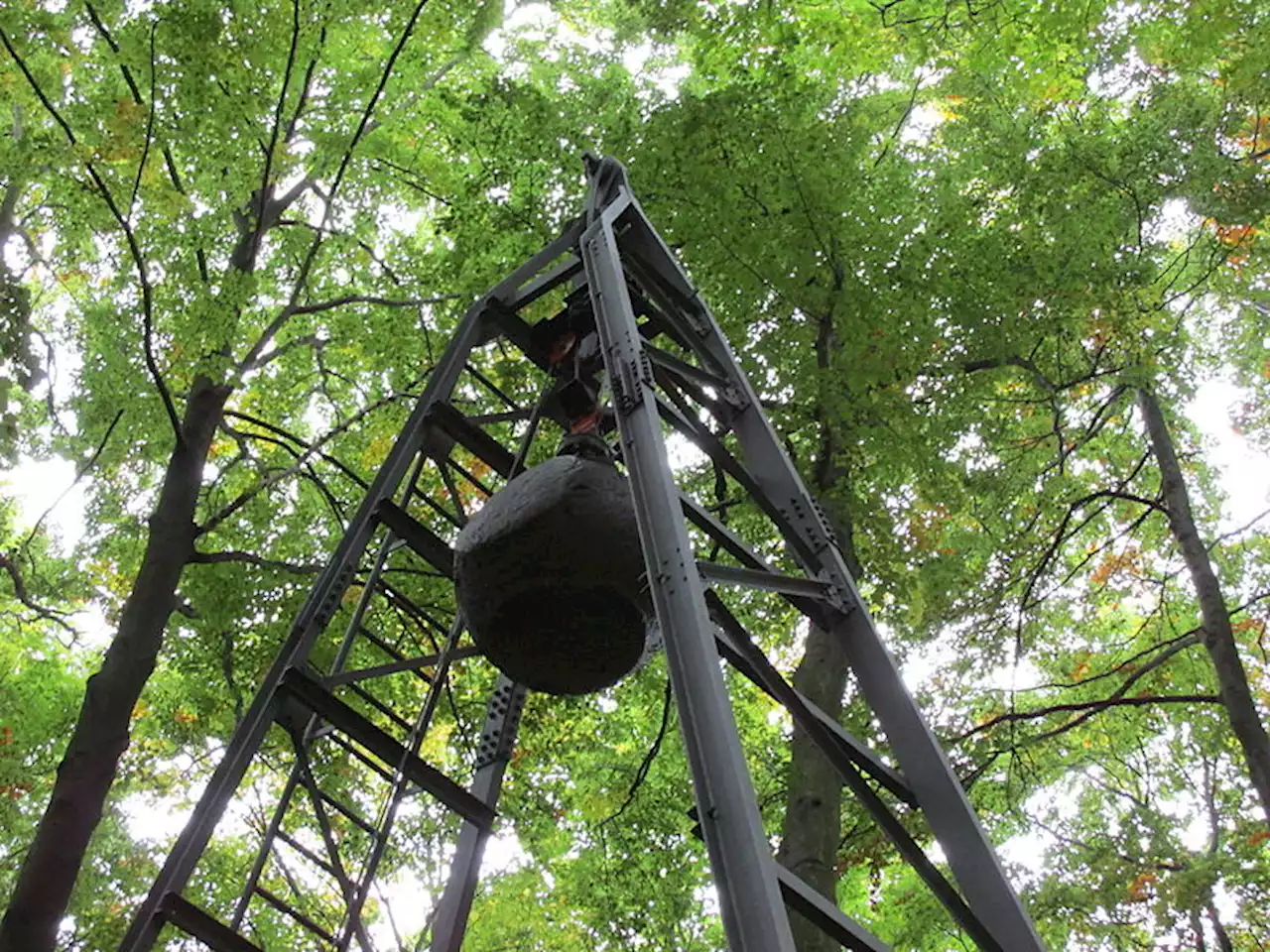
An old seismological station in Germany holds the history of the modern geophysics field.
He also argued that the Earth has a heavy iron core. Weichert invited many leading scientists in the field of geophysics to join him at the station. One of particular note was the German physicist namedMintrop was a dedicated student of Wiechert, he would also go on to be known as one of the founding figures of modern geophysics. He is most famous for his 1908 invention that can artificially produce earthquakes.
The collected data can then be used to determine the geological structure underneath the surface. His invention consists of a 14-meter tall steel scaffolding rig, from which a 4-ton steel ball was dropped into the bedrock of shell limestone below. Portable seismographs on site were then used to measure the seismic reactions of the ball dropping at various distances away from the fall site.
The data also allowed him to make a hypothesis about the exact nature of geological structures near the surface. Mintrop developed this technology and used it to form the geological exploration companyThe iron ball was later replaced by dynamite. This method of geological exploration is still used today by large oil companies to search for deposits of crude oil, natural gas, and other minerals. Mintrop’s original experiment site is still present at Hainberg, albeit with a few modern upgrades.
The ball is now raised up with an electric motor and has a remote release mechanism. But visitors to the seismic research center can still watch the experiment be carried out.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 The Late Permian Mass Extinction ExplainedBurning coal caused the largest mass extinction in earth’s history — the Late Permian Mass Extinction, or the Great Dying.
The Late Permian Mass Extinction ExplainedBurning coal caused the largest mass extinction in earth’s history — the Late Permian Mass Extinction, or the Great Dying.
Lire la suite »
 How the 'wickedest city on Earth' was sunk by an earthquakeJamaica's Port Royal was the Caribbean's most notorious pirate haven when it sank into the sea in 1692. Centuries later, underwater archaeologists unearthed fascinating stories from its ruins.
How the 'wickedest city on Earth' was sunk by an earthquakeJamaica's Port Royal was the Caribbean's most notorious pirate haven when it sank into the sea in 1692. Centuries later, underwater archaeologists unearthed fascinating stories from its ruins.
Lire la suite »
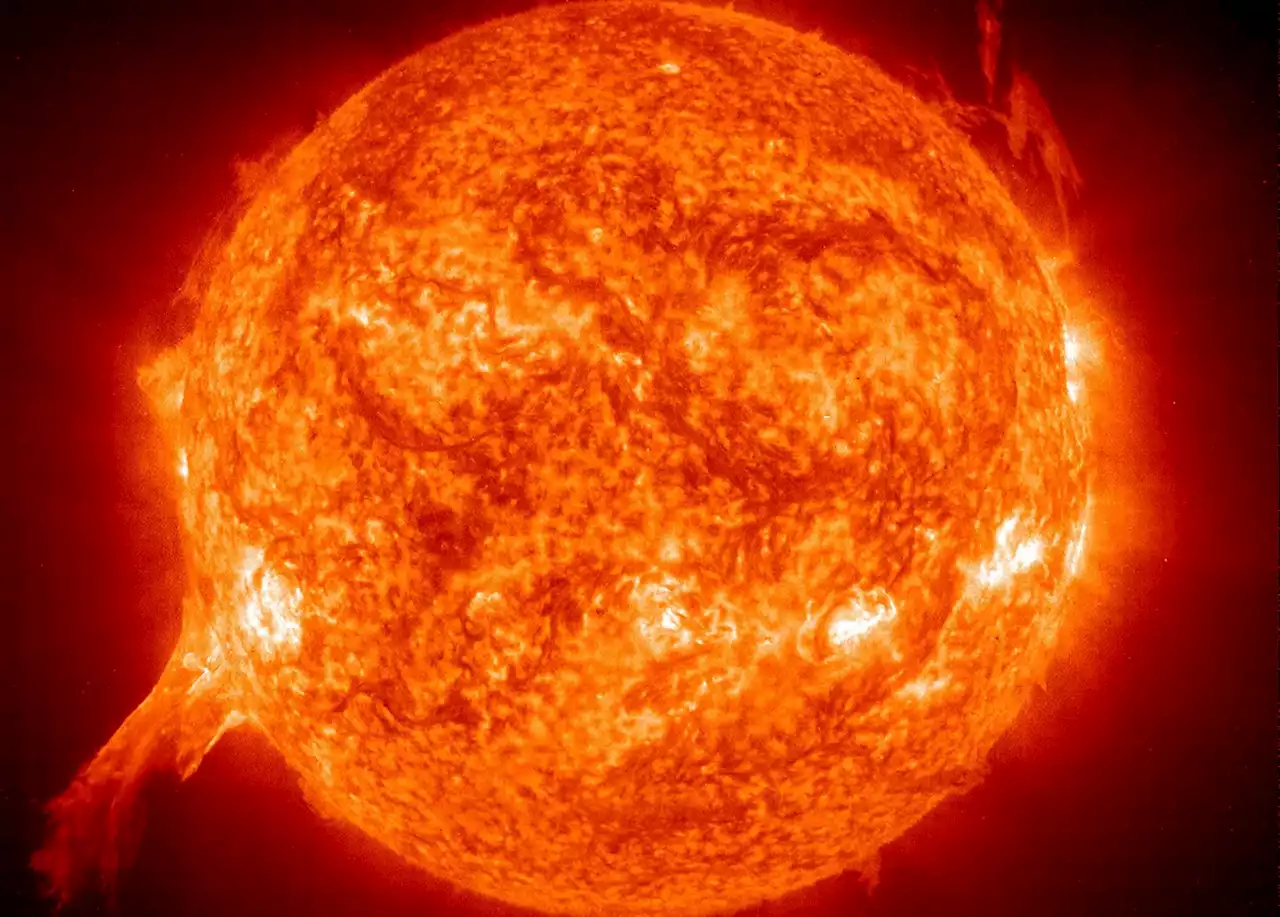 New, huge sunspot triples in size in 24 hoursSunspots, caused by the sun's tangled magnetic field, can eject solar material towards Earth resulting in geomagnetic storms.
New, huge sunspot triples in size in 24 hoursSunspots, caused by the sun's tangled magnetic field, can eject solar material towards Earth resulting in geomagnetic storms.
Lire la suite »
![]() Joining the Effort to Make Sensor Sizes Less ConfusingThe naming convention of small sensors is confusing and misleading. In an effort to help make them more easily understood, we’re changing our editorial guidelines and moving away from using “inch” to describe their size.
Joining the Effort to Make Sensor Sizes Less ConfusingThe naming convention of small sensors is confusing and misleading. In an effort to help make them more easily understood, we’re changing our editorial guidelines and moving away from using “inch” to describe their size.
Lire la suite »
 Illinois has the most Muslims per capita in the U.S., and a new report takes a deep dive into this expansive communityA report three years in the making takes a deep dive into the community to help leaders better understand how to serve the state’s fast-growing and diverse Muslim population.
Illinois has the most Muslims per capita in the U.S., and a new report takes a deep dive into this expansive communityA report three years in the making takes a deep dive into the community to help leaders better understand how to serve the state’s fast-growing and diverse Muslim population.
Lire la suite »
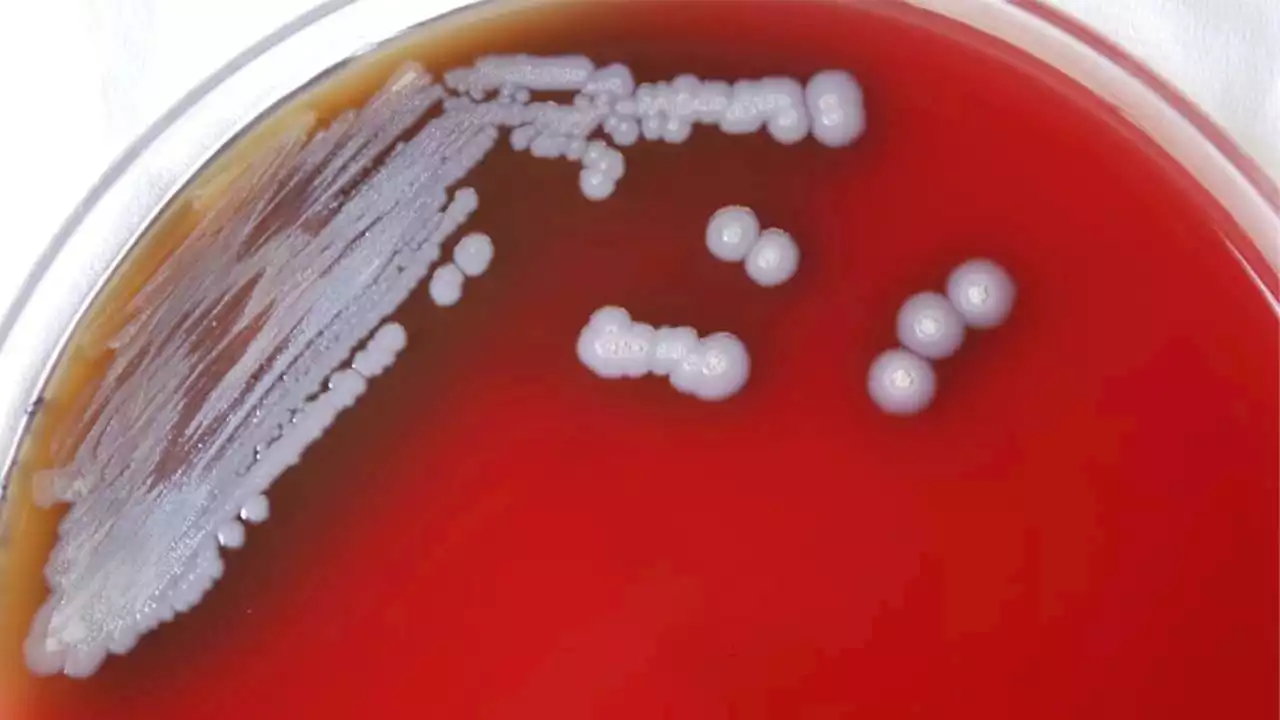 Bacteria that causes rare tropical disease found in US soilA rare and sometimes deadly bacteria - long thought to be confined to tropical climates - has been found in soil and water in the continental United States
Bacteria that causes rare tropical disease found in US soilA rare and sometimes deadly bacteria - long thought to be confined to tropical climates - has been found in soil and water in the continental United States
Lire la suite »
