Study implicates gut microbiome health in Parkinson's disease Microbiome Parkinsons Disease Gut Metagenomics NatureComms UABNews asap_research UniOfSurrey EmoryMedicine
By Dr. Liji Thomas, MDDec 1 2022Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative condition that hampers movement and ultimately results in the loss of independence.
Several causes may underlie PD, including genetic susceptibility and environmental risk factors. In most cases, no cause is identifiable. However, Braak's hypothesis traces non-familial PD to gut infection, following a long-known pattern of constipation, loss of epithelial barrier integrity in the gut, and inflammation. In addition, early PD has been associated with the presence of alpha-synuclein bodies within gut cells.
The current paper is based on metagenomics, which implies using all the genetic matter obtained from a community of organisms. The study aimed to provide a large-scale view of how the gut microbiome was altered in PD. It was carried out by researchers in the NeuroGenetics Research Consortium, NGRC, using a large number of samples and deep sequencing.
What did the study show? The researchers found several striking findings. Not only did the results confirm that dysbiosis is frequent and significant in PD patients, but they also identified the species responsible for such dysbiosis. Overall, the scientists showed that many species changed in abundance, with opportunistic pathogens becoming overabundant. In addition, immunogenic molecules were also produced. These could induce inflammation and infection, along with the overproduction of toxic molecules and curli.
The scientists also found several co-occurring species as well as those that show reciprocal changes in abundance. They found several species to be depleted, including those like Roseburia species and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, that produce short-chain fatty acids . The study also resolved some contradictory findings from earlier research, showing they were due to false assumptions of homogeneity across genera in a given disease. Thus, both Prevotella and Streptococci were found to comprise different species, some of which increased and others decreased in association with PD.
Again, genes encoding the breakdown of proteins and amino acids were enriched in PD, indicating a shift to using these molecules for energy or as carbon sources instead of sugars. Mucin is one such source, and increased mucin degradation could contribute to the increased gut permeability in PD.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Metagenomics of Parkinson’s disease implicates the gut microbiome in multiple disease mechanisms - Nature CommunicationsHere, the authors perform large-scale high-resolution Parkinson’s disease metagenomics analyses, revealing widespread dysbiosis characterized by overabundance of pathogens, immunogens, toxicants, and curli, reduction in neuroprotective and antiinflammatory molecules, and dysregulated neuroactive signaling.
Metagenomics of Parkinson’s disease implicates the gut microbiome in multiple disease mechanisms - Nature CommunicationsHere, the authors perform large-scale high-resolution Parkinson’s disease metagenomics analyses, revealing widespread dysbiosis characterized by overabundance of pathogens, immunogens, toxicants, and curli, reduction in neuroprotective and antiinflammatory molecules, and dysregulated neuroactive signaling.
Lire la suite »
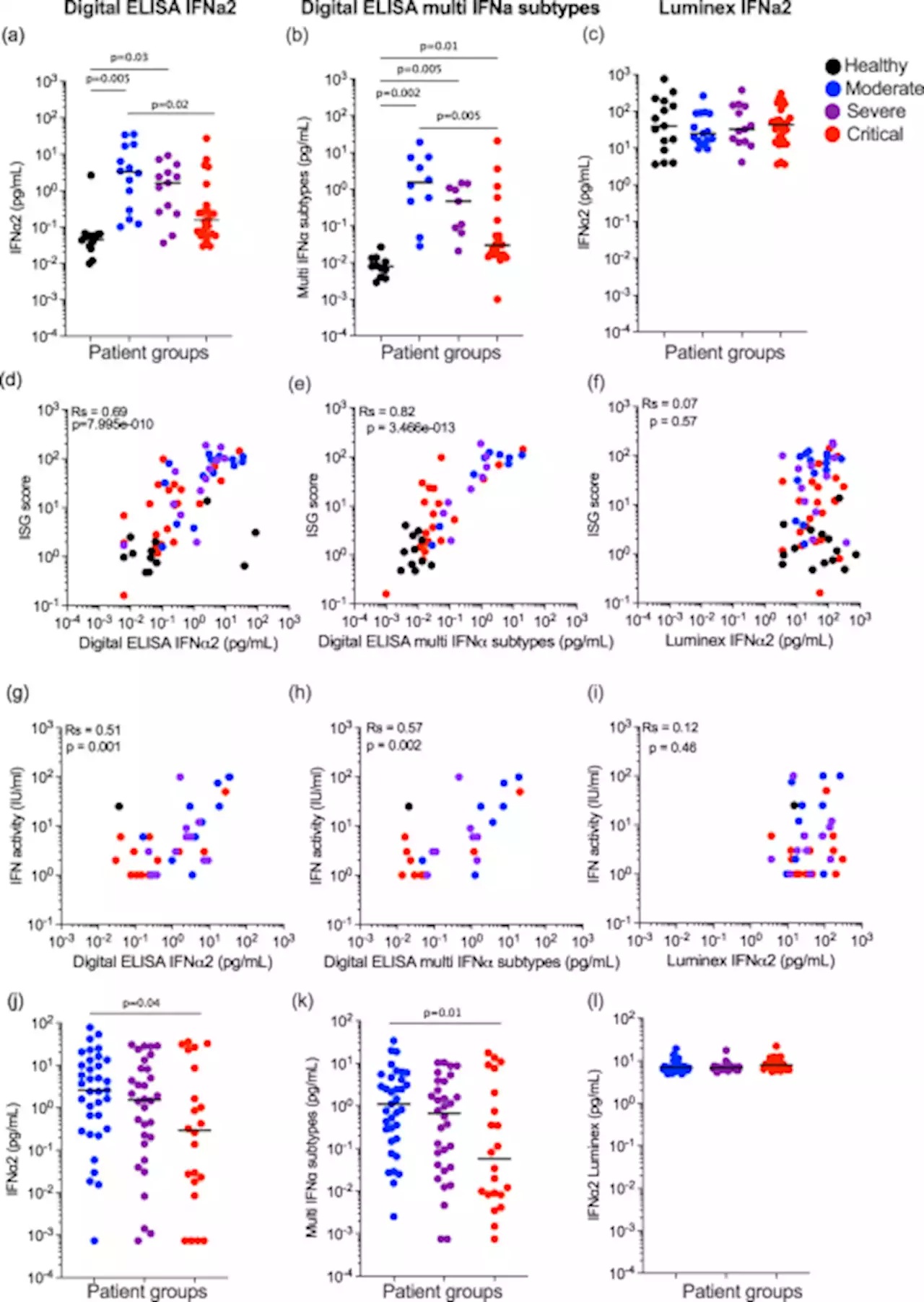 Defective activation and regulation of type I interferon immunity is associated with increasing COVID-19 severity - Nature CommunicationsThe interferon response has been shown to be linked to severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection and is an essential component of the immune response to COVID-19. Here the authors stratify patients according to COVID-19 severity and asses the interferon response showing defective responses in severe infection and highlight the importance of assay variables and confounding factors that impact the detection of interferon.
Defective activation and regulation of type I interferon immunity is associated with increasing COVID-19 severity - Nature CommunicationsThe interferon response has been shown to be linked to severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection and is an essential component of the immune response to COVID-19. Here the authors stratify patients according to COVID-19 severity and asses the interferon response showing defective responses in severe infection and highlight the importance of assay variables and confounding factors that impact the detection of interferon.
Lire la suite »
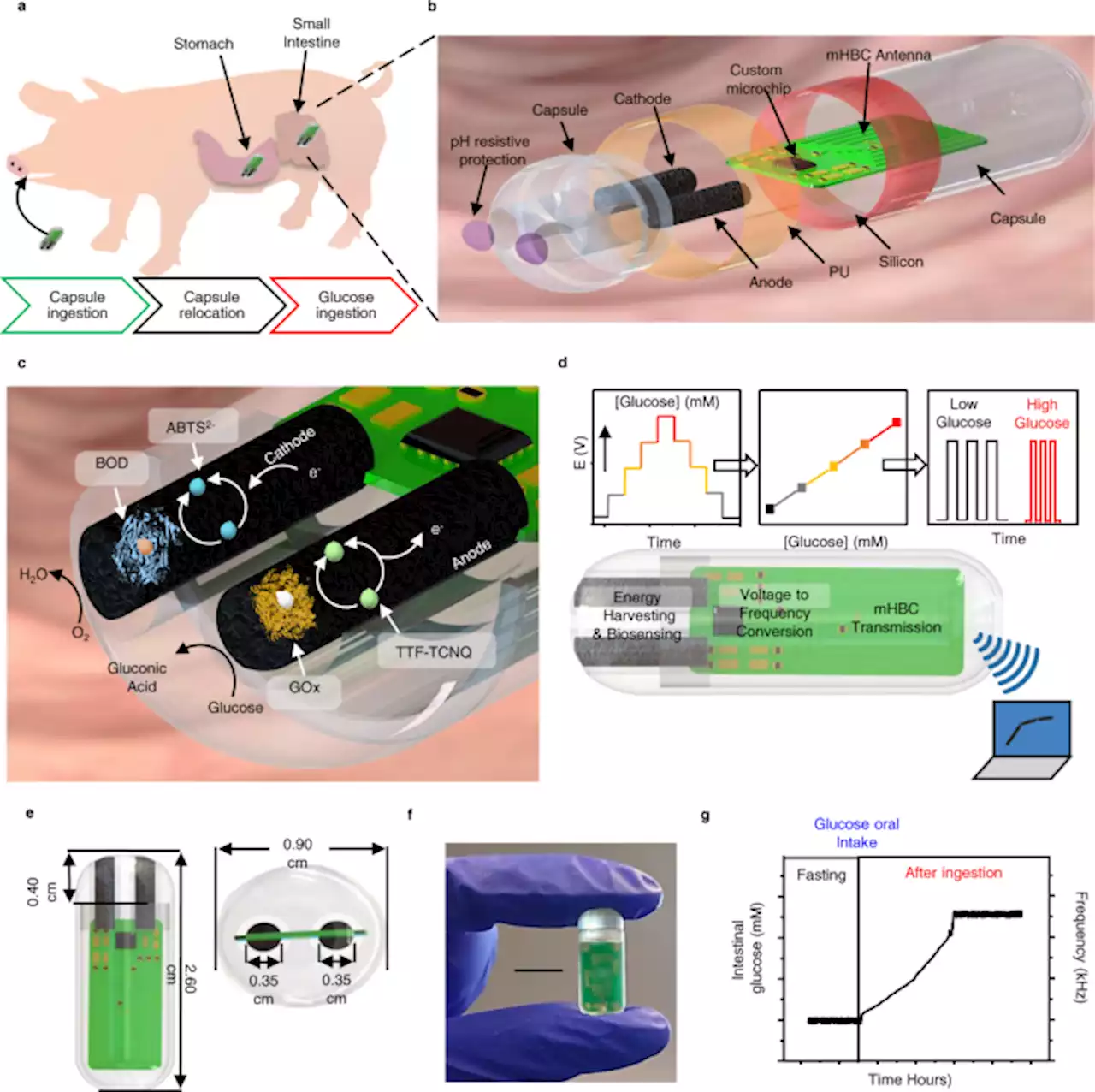 A self-powered ingestible wireless biosensing system for real-time in situ monitoring of gastrointestinal tract metabolites - Nature CommunicationsMetabolic dynamics within the small intestine are difficult to study due to the lack of in situ access. Here, the authors report an ingestible, self-powered, and wireless biosensing system, demonstrating proof-of-principle real-time glucose monitoring in the small intestines of pigs.
A self-powered ingestible wireless biosensing system for real-time in situ monitoring of gastrointestinal tract metabolites - Nature CommunicationsMetabolic dynamics within the small intestine are difficult to study due to the lack of in situ access. Here, the authors report an ingestible, self-powered, and wireless biosensing system, demonstrating proof-of-principle real-time glucose monitoring in the small intestines of pigs.
Lire la suite »
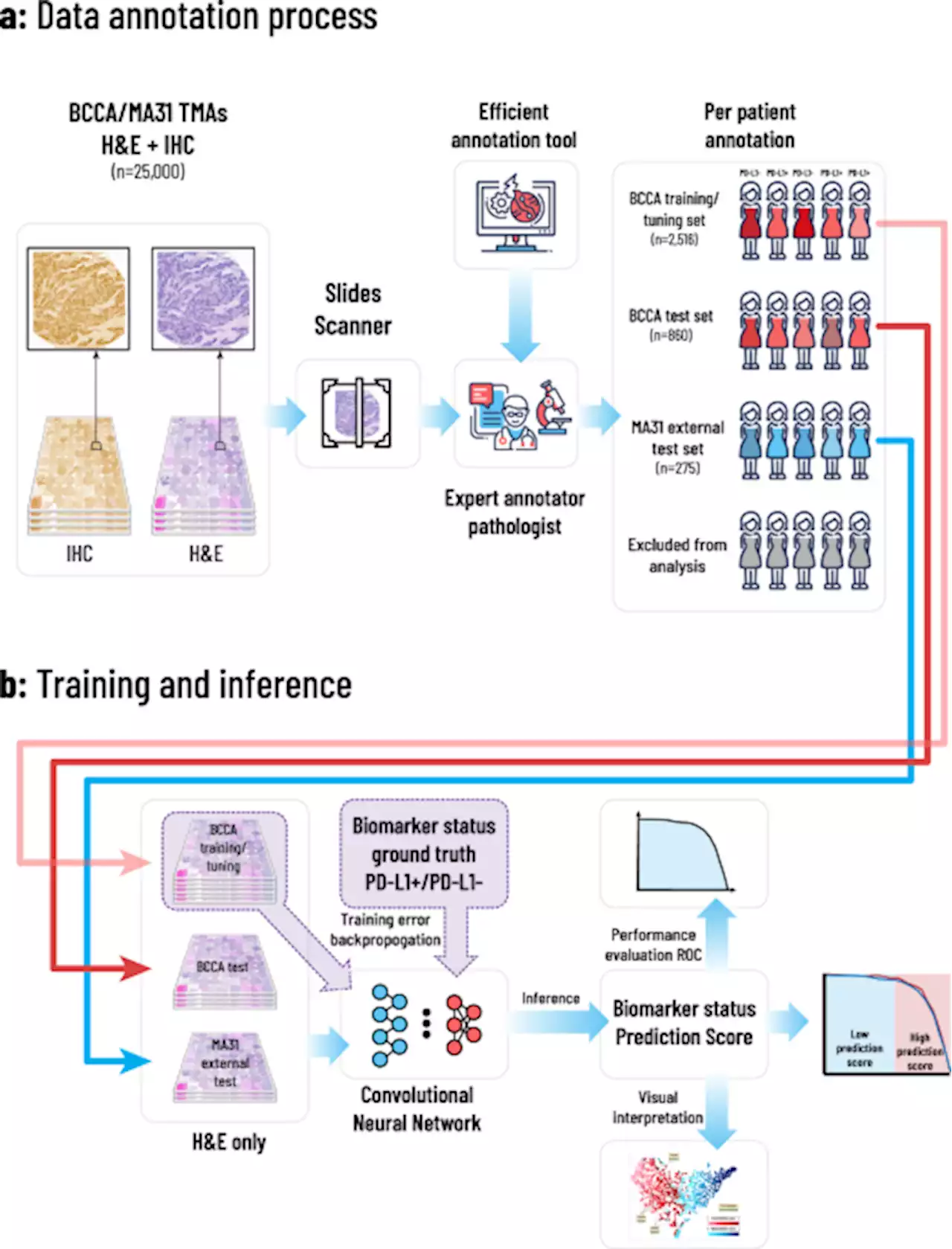 Deep learning-based image analysis predicts PD-L1 status from H&E-stained histopathology images in breast cancer - Nature CommunicationsProgrammed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) has been recently adopted for breast cancer as a predictive biomarker for immunotherapies. Here, the authors show that PD-L1 expression can be predicted from H&E-stained images using deep learning.
Deep learning-based image analysis predicts PD-L1 status from H&E-stained histopathology images in breast cancer - Nature CommunicationsProgrammed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) has been recently adopted for breast cancer as a predictive biomarker for immunotherapies. Here, the authors show that PD-L1 expression can be predicted from H&E-stained images using deep learning.
Lire la suite »
 Government ‘failing to keep promises’ on restoring nature – Wildlife TrustsThe Government has come under fire for its record of “failing to keep promises” on the environment ahead of global talks aimed at reversing nature losses.
Government ‘failing to keep promises’ on restoring nature – Wildlife TrustsThe Government has come under fire for its record of “failing to keep promises” on the environment ahead of global talks aimed at reversing nature losses.
Lire la suite »
 Expanding freedom to roam to woods could ‘unlock’ nature for poor communitiesThe poorest communities would have access to nature an average of just 20 minutes’ walk away if the freedom to roam included woodlands, campaigners claim. They're calling on the government to add woodland to the law.
Expanding freedom to roam to woods could ‘unlock’ nature for poor communitiesThe poorest communities would have access to nature an average of just 20 minutes’ walk away if the freedom to roam included woodlands, campaigners claim. They're calling on the government to add woodland to the law.
Lire la suite »