U.S. report lays out an ambitious plan to harness the “RNome” for medicine and more—but funding is uncertain
Among the 10 bases in this RNA molecule from SARS-CoV-2, two have modifications that likely affect the RNA’s function.In 2021, as a new kind of vaccine began to protect millions from COVID-19, many people heard about messenger RNA for the first time since high school biology. The molecule, which transfers DNA’s code out of a cell’s nucleus to guide protein production, is just one of several types of RNA that profoundly affect how cells function. Now, the U.S.
Far from being just a messenger for genetic information, RNA serves diverse roles in cells. Transfer RNA delivers specific amino acids to the ribosome—also partly composed of RNA—that puts together proteins. Other RNAs silence genes or affect their activity. How these RNAs behave reflects not just their sequence, but also how they are modified before being exported from the cell’s nucleus, often by the addition of chemical side groups.
It sets a series of 5-year goals and suggests the establishment of “RNA core centers” to tackle them. Over 10 years, the RNome project should document all the modifications in the RNA of a few well-characterized human cell lines. By 15 years, it should have mapped modifications under different conditions in model organisms such as worms and cataloged them in human diseases.
Other NASEM suggestions tackle research methods: The National Institute of Standards and Technology must come up with synthetic RNA molecules, with known modifications in known places, that researchers can use as a reference to test their sequencing technologies and lab protocols, the report says. The National Institutes of Health , working with international partners, should establish a centralized database for RNAs, along with rules about how to describe them.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Modeling the origins of life: New evidence for an 'RNA World'Scientists provide fresh insights on the origins of life, presenting compelling evidence supporting the 'RNA World' hypothesis. The study unveils an RNA enzyme that can make accurate copies of other functional RNA strands, while also allowing new variants of the molecule to emerge over time.
Modeling the origins of life: New evidence for an 'RNA World'Scientists provide fresh insights on the origins of life, presenting compelling evidence supporting the 'RNA World' hypothesis. The study unveils an RNA enzyme that can make accurate copies of other functional RNA strands, while also allowing new variants of the molecule to emerge over time.
Lire la suite »
 RNA-based therapy shows promise against aggressive childhood brain tumors in miceTargeting a non-encoding stretch of RNA may help shrink tumors caused by an aggressive type of brain cancer in children, according to new research in mice.
RNA-based therapy shows promise against aggressive childhood brain tumors in miceTargeting a non-encoding stretch of RNA may help shrink tumors caused by an aggressive type of brain cancer in children, according to new research in mice.
Lire la suite »
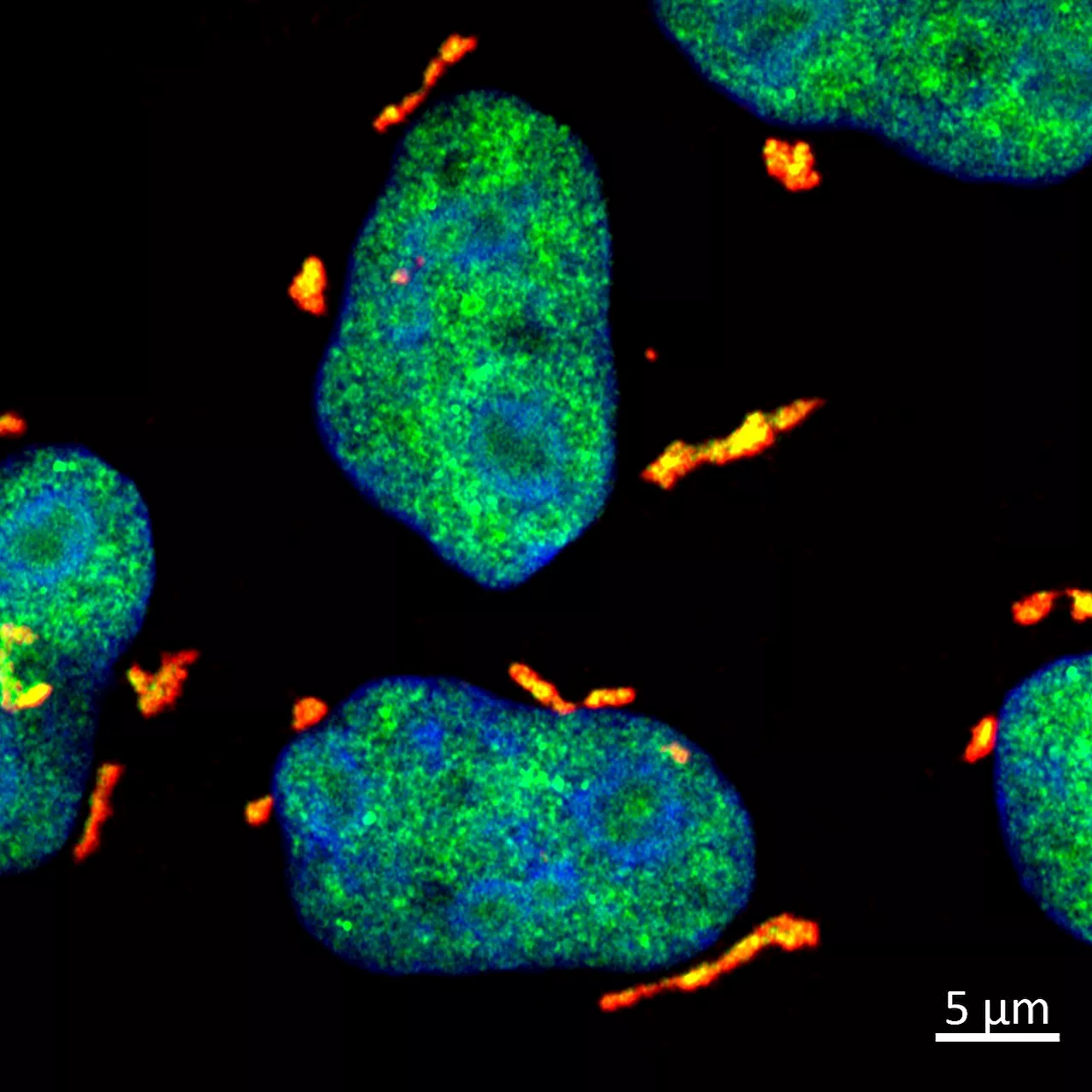 How DHX9 stress granules protect daughter cells from UV-induced RNA damageDuring the process of cell division, new daughter cells inherit a mix of genetic material and other molecules from their mother cells.
How DHX9 stress granules protect daughter cells from UV-induced RNA damageDuring the process of cell division, new daughter cells inherit a mix of genetic material and other molecules from their mother cells.
Lire la suite »
 mRNA vaccines may make unintended proteins, but there’s no evidence of harmAlterations that help messenger RNA persist in living cells can trip up protein synthesis
mRNA vaccines may make unintended proteins, but there’s no evidence of harmAlterations that help messenger RNA persist in living cells can trip up protein synthesis
Lire la suite »
 ‘It’s insane’: New viruslike entities found in human gut microbesAnalysis of sequence databases reveals novel circular RNA genomes belonging to “obelisks”
‘It’s insane’: New viruslike entities found in human gut microbesAnalysis of sequence databases reveals novel circular RNA genomes belonging to “obelisks”
Lire la suite »
 Development of novel aptamers unlocks opportunities for the treatment of cancers and neurological diseasesG-quadruplexes (G4), which are special structures in DNA and RNA that play a crucial role in cells, have been associated with cancers and neurological diseases. A research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently built a new platform to select L-RNA aptamers that can target functional G4 structures.
Development of novel aptamers unlocks opportunities for the treatment of cancers and neurological diseasesG-quadruplexes (G4), which are special structures in DNA and RNA that play a crucial role in cells, have been associated with cancers and neurological diseases. A research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently built a new platform to select L-RNA aptamers that can target functional G4 structures.
Lire la suite »
