New research has improved the accuracy of the parameters governing the expansion of the Universe. More accurate parameters will help astronomers determine how the Universe grew to its current state, and how it will evolve in the future.
It is well established that the Universe is expanding. But with no landmarks in space, it is difficult to accurately measure how fast it is expanding. So, astronomers search for reliable landmarks. The same way a candle looks fainter as it gets farther away, even though the candle itself hasn't changed, distant objects in the Universe look fainter. If we know the intrinsic brightness of an object, we can calculate its distance based on its observed brightness.
An international team led by Maria Giovanna Dainotti, Assistant Professor at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan , and Giada Bargiacchi, PhD student at the Scuola Superiore Meridionale in Naples, with the aid of the supercomputing facilities at NAOJ run by Kazunari Iwasaki, Assistant Professor at NAOJ and member of the Center for Computational Astrophysics, ushered in a new research field by leveraging the use of a variety of new statistical methods to analyze data for various...
The new results reduce the uncertainty of key parameters by up to 35 percent. More accurate parameters will help determine whether the Universe will continue expanding forever, or eventually fall back in on itself.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Study observes sudden acceleration of flow, generates new boundary layer -- ScienceDailyIn an experiment on how turbulent boundary layers respond to acceleration in the flow around them, aerospace engineers at the observed an unexpected internal boundary layer.
Study observes sudden acceleration of flow, generates new boundary layer -- ScienceDailyIn an experiment on how turbulent boundary layers respond to acceleration in the flow around them, aerospace engineers at the observed an unexpected internal boundary layer.
Lire la suite »
 Study uncovers potential new source of genetic mutations that cause neurodegenerative disease -- ScienceDailyAn international team of scientists has discovered an additional potential cause of the genetic mutations that result in rare neurodegenerative conditions such as Huntington's disease.
Study uncovers potential new source of genetic mutations that cause neurodegenerative disease -- ScienceDailyAn international team of scientists has discovered an additional potential cause of the genetic mutations that result in rare neurodegenerative conditions such as Huntington's disease.
Lire la suite »
 New insights into fighting antimicrobial resistance -- ScienceDailyCooking food thoroughly and avoiding some types of vegetables and salad during a course of antibiotic treatment could potentially reduce antibiotic resistance, by preventing bacteria carrying resistance genes getting into the gut, according to a new study.
New insights into fighting antimicrobial resistance -- ScienceDailyCooking food thoroughly and avoiding some types of vegetables and salad during a course of antibiotic treatment could potentially reduce antibiotic resistance, by preventing bacteria carrying resistance genes getting into the gut, according to a new study.
Lire la suite »
 A new way to identify chiral molecules with light could vastly improve detection efficiency -- ScienceDailyResearchers have proposed a highly efficient method for detecting molecular chirality using tailored laser fields.
A new way to identify chiral molecules with light could vastly improve detection efficiency -- ScienceDailyResearchers have proposed a highly efficient method for detecting molecular chirality using tailored laser fields.
Lire la suite »
 Energy and heat transfer: A new 'spin' on ergodicity breaking -- ScienceDailyScientists have observed novel ergodicity-breaking in C60, a highly symmetric molecule composed of 60 carbon atoms arranged on the vertices of a 'soccer ball' pattern (with 20 hexagon faces and 12 pentagon faces). Their results revealed ergodicity breaking in the rotations of C60. Remarkably, they found that this ergodicity breaking occurs without symmetry breaking and can even turn on and off as the molecule spins faster and faster. Understanding ergodicity breaking can help scientists design better-optimized materials for energy and heat transfer.
Energy and heat transfer: A new 'spin' on ergodicity breaking -- ScienceDailyScientists have observed novel ergodicity-breaking in C60, a highly symmetric molecule composed of 60 carbon atoms arranged on the vertices of a 'soccer ball' pattern (with 20 hexagon faces and 12 pentagon faces). Their results revealed ergodicity breaking in the rotations of C60. Remarkably, they found that this ergodicity breaking occurs without symmetry breaking and can even turn on and off as the molecule spins faster and faster. Understanding ergodicity breaking can help scientists design better-optimized materials for energy and heat transfer.
Lire la suite »
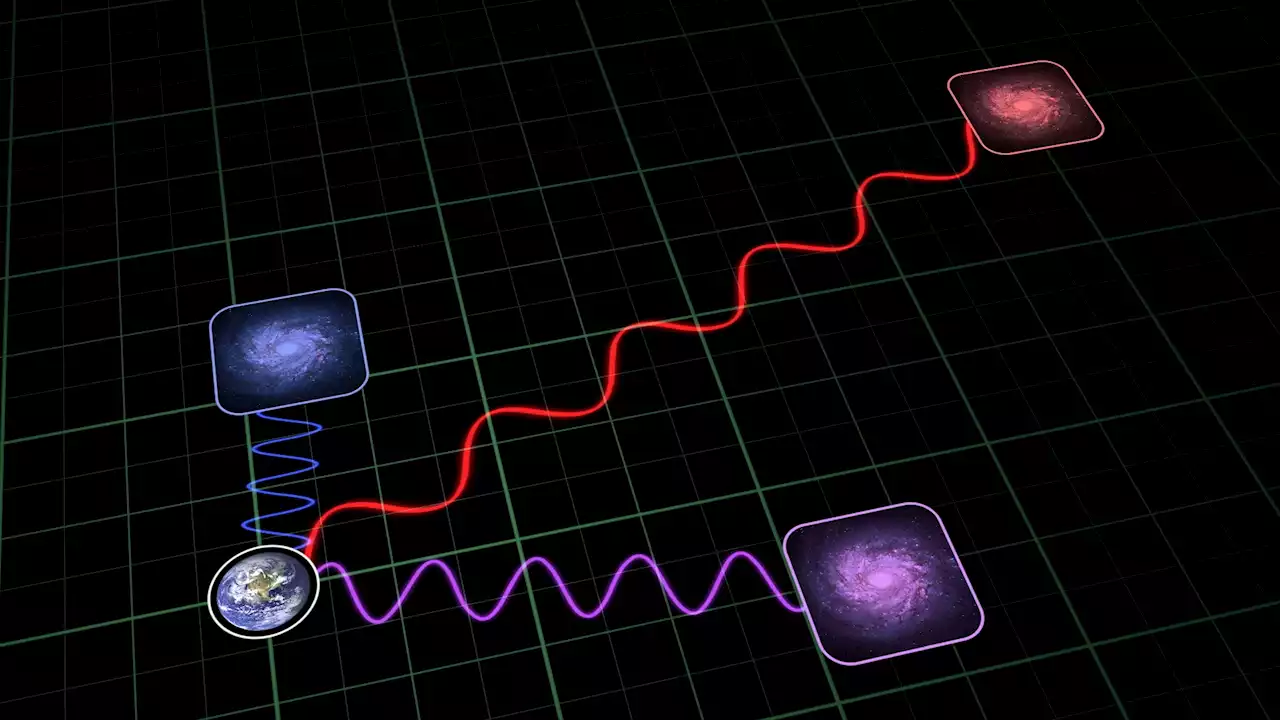 A New Way to Measure the Expansion Rate of the Universe: Redshift DriftAlmost all the galaxies in the Universe are speeding away from us because of the Big Bang and the acceleration of dark energy. One technique to measure this expansion is redshift, seeing how light is reddened over time as its wavelength stretches out. But every observation astronomers can make is a snapshot, measuring the redshift now. But an intriguing idea is to measure how the redshift changes over time as a galaxy's movement accelerates. It's called 'redshift drift' and requires an exact series of measurements over time.
A New Way to Measure the Expansion Rate of the Universe: Redshift DriftAlmost all the galaxies in the Universe are speeding away from us because of the Big Bang and the acceleration of dark energy. One technique to measure this expansion is redshift, seeing how light is reddened over time as its wavelength stretches out. But every observation astronomers can make is a snapshot, measuring the redshift now. But an intriguing idea is to measure how the redshift changes over time as a galaxy's movement accelerates. It's called 'redshift drift' and requires an exact series of measurements over time.
Lire la suite »
