Modified CRISPR-based enzymes improve the prospect of inserting entire genes into the genome NatureBiotech
CRISPR-associated transposases enable recombination-independent, multi-kilobase DNA insertions at RNA-programmed genomic locations. However, the utility of type V-K CASTs is hindered by high off-target integration and a transposition mechanism that results in a mixture of desired simple cargo insertions and undesired plasmid cointegrate products. Here we overcome both limitations by engineering new CASTs with improved integration product purity and genome-wide specificity.
enables cut-and-paste DNA insertion with up to 99.4% simple insertion product purity, while retaining robust integration efficiencies on genomic targets. has substantially higher on-target specificity than canonical CASTs, and we identify several novel factors that further regulate targeted and genome-wide integration. Finally, we extend
to other type V-K orthologs and demonstrate the feasibility of -mediated integration in human cell contexts.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Artist connects people to nature using Lego bricksLarge-than-life Lego sculptures examine the relationship between humans and nature at Nature Connects.
Artist connects people to nature using Lego bricksLarge-than-life Lego sculptures examine the relationship between humans and nature at Nature Connects.
Lire la suite »
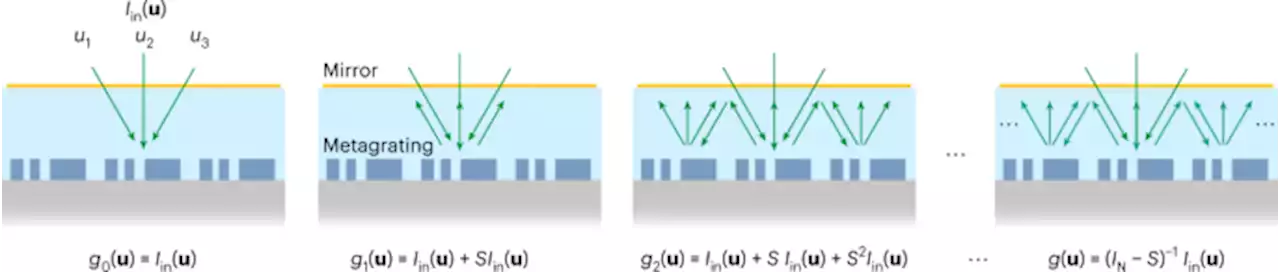 Solving integral equations in free space with inverse-designed ultrathin optical metagratings - Nature NanotechnologyMetasurfaces can solve Fredholm integral equations of the second kind for free-space radiation at optical wavelengths. To this end, an inverse-designed metagrating is coupled to a semitransparent mirror providing feedback to perform an analogue version of the Neumann series.
Solving integral equations in free space with inverse-designed ultrathin optical metagratings - Nature NanotechnologyMetasurfaces can solve Fredholm integral equations of the second kind for free-space radiation at optical wavelengths. To this end, an inverse-designed metagrating is coupled to a semitransparent mirror providing feedback to perform an analogue version of the Neumann series.
Lire la suite »
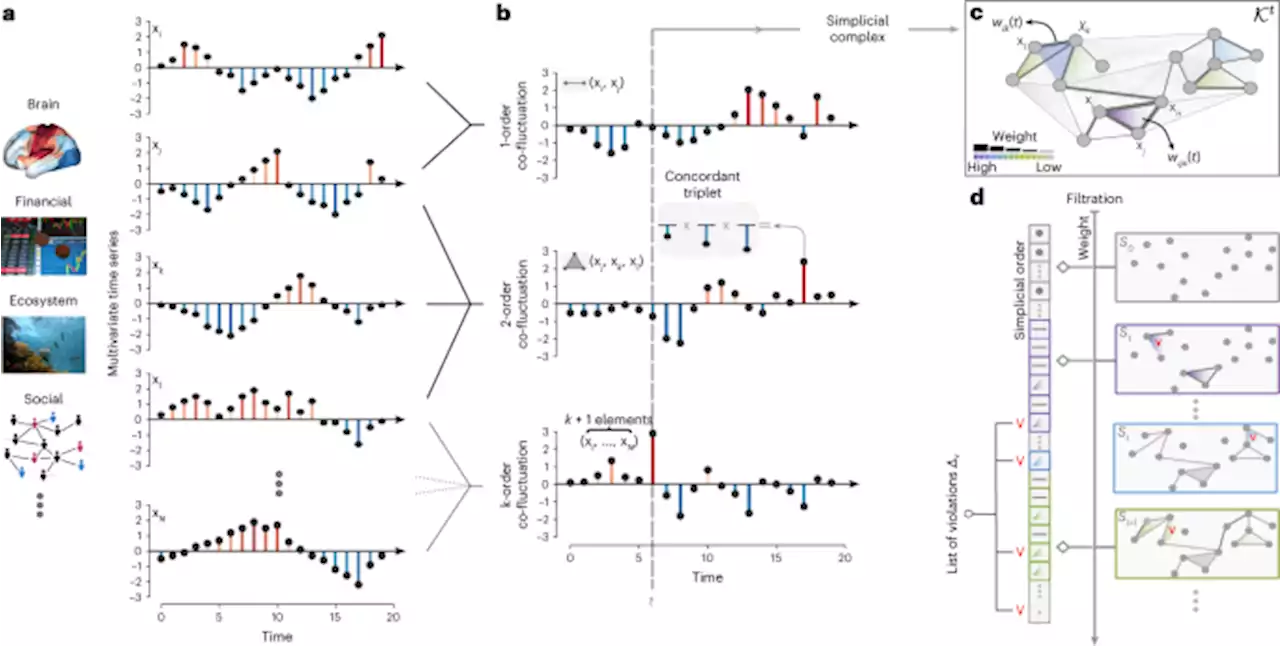 Higher-order organization of multivariate time series - Nature PhysicsMost temporal analyses of multivariate time series rely on pairwise statistics. A study combining network theory and topological data analysis now shows how to characterize the dynamics of signals at all orders of interactions in real-world data.
Higher-order organization of multivariate time series - Nature PhysicsMost temporal analyses of multivariate time series rely on pairwise statistics. A study combining network theory and topological data analysis now shows how to characterize the dynamics of signals at all orders of interactions in real-world data.
Lire la suite »
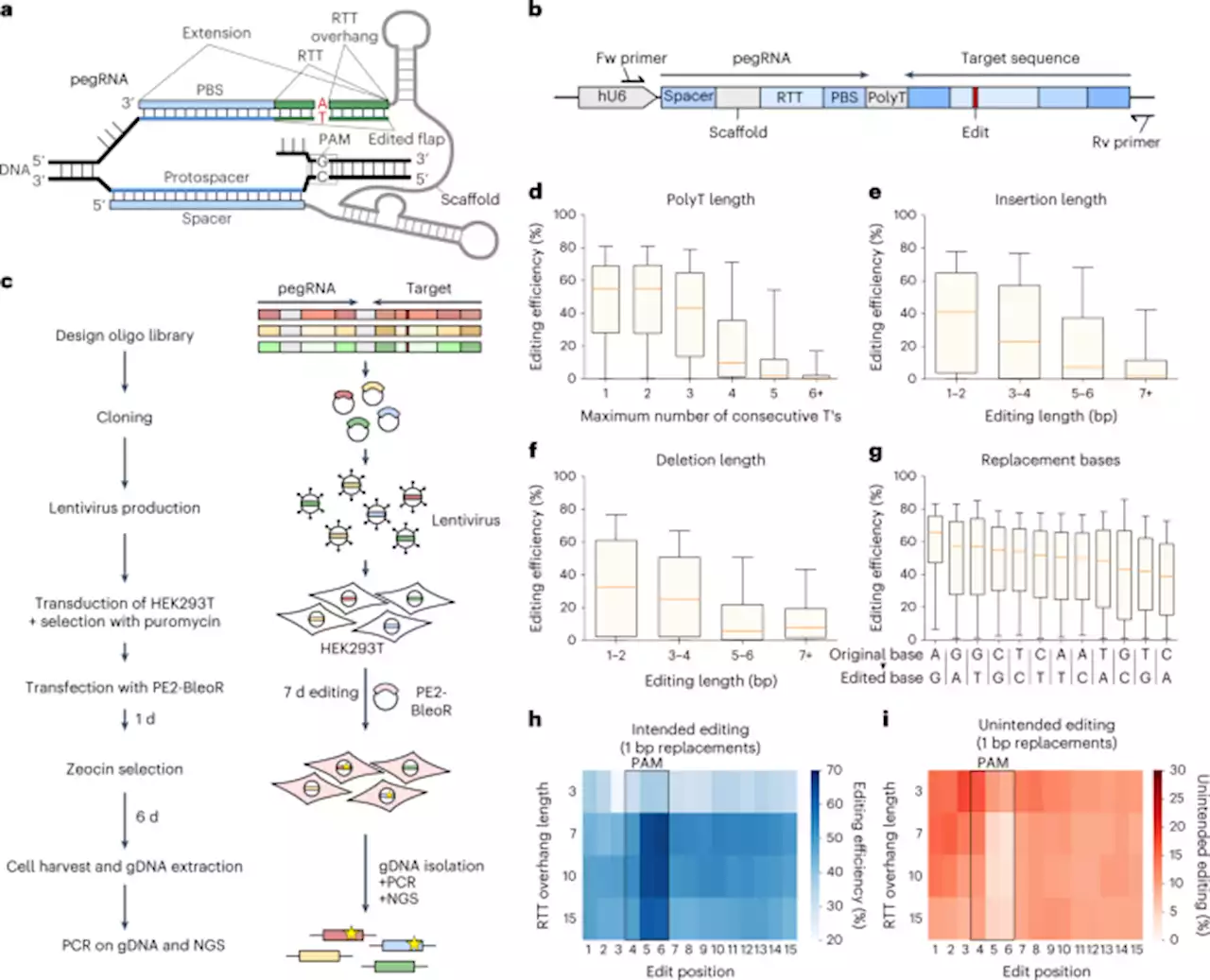 Predicting prime editing efficiency and product purity by deep learning - Nature BiotechnologyPredicting prime editing efficiency and product purity by deep learning
Predicting prime editing efficiency and product purity by deep learning - Nature BiotechnologyPredicting prime editing efficiency and product purity by deep learning
Lire la suite »
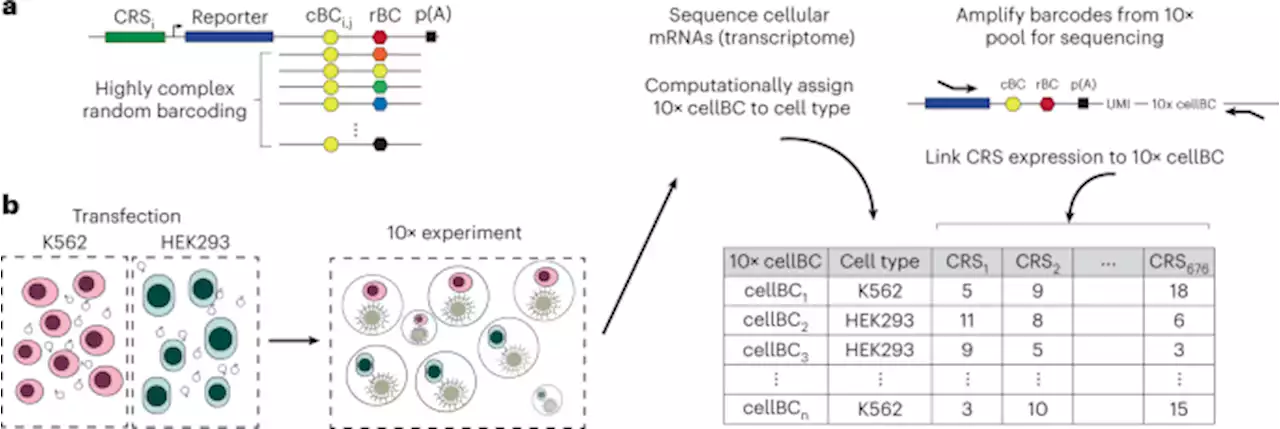 A single-cell massively parallel reporter assay detects cell-type-specific gene regulation - Nature GeneticsA single-cell massively parallel reporter assay is used to compare cis-regulatory sequence activities in cell line models and mouse retinal tissue ex vivo, identifying cell state- and cell-type-specific effects of sequence variation.
A single-cell massively parallel reporter assay detects cell-type-specific gene regulation - Nature GeneticsA single-cell massively parallel reporter assay is used to compare cis-regulatory sequence activities in cell line models and mouse retinal tissue ex vivo, identifying cell state- and cell-type-specific effects of sequence variation.
Lire la suite »
 Electrochemically modulated interaction of MXenes with microwaves - Nature NanotechnologyModulating the interaction of a thin film with microwaves is realized using the electrochemical behaviours of various MXenes.
Electrochemically modulated interaction of MXenes with microwaves - Nature NanotechnologyModulating the interaction of a thin film with microwaves is realized using the electrochemical behaviours of various MXenes.
Lire la suite »
