Science, Space and Technology News 2024
The tiny roundworm C.elegans is the focus of a new study examining 3’UTRs. These short segments of RNA play a critical role in the regulation of genes. The resulting map, the product of 20 years of research, is the most complete dataset of its kind for any animal, and will help advance basic understanding of mechanisms of gene regulation critical in human health and disease. Credit: Graphic by Jason Dreeshave made a major breakthrough in understanding gene regulation in living organisms.
Marco Mangone is a researcher in the Biodesign Virginia G. Piper Center for Personalized Diagnostics and a professor in the School of Life Sciences at ASU. Credit: The Biodesign Institute at Arizona State University 3’UTRs are sections of RNA located at the end of a messenger RNA molecule. They help to govern how and when proteins are made by controlling the stability and efficiency of the mRNA. This regulation allows for dynamic responses to environmental changes and enables control over protein production, which is essential for adapting to various physiological needs.Initially, noncoding RNAs like 3’UTRs were regarded as nonessential genetic fragments because they themselves do not code for proteins.
These characteristics make C. elegans a powerful tool for uncovering fundamental mechanisms of biology that are often conserved acrossThe study found that the process of switching between different 3’UTRs is less common in C. elegans than previously thought. This challenges earlier beliefs and highlights the complexity of gene regulation. Using the new data, scientists updated predictions for how microRNAs interact with genes.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 New map offers guide to free public bathrooms across New York CityResidents can now access a map both in their hands and on their phone which shows them every free public restroom available for use in New York City.
New map offers guide to free public bathrooms across New York CityResidents can now access a map both in their hands and on their phone which shows them every free public restroom available for use in New York City.
Lire la suite »
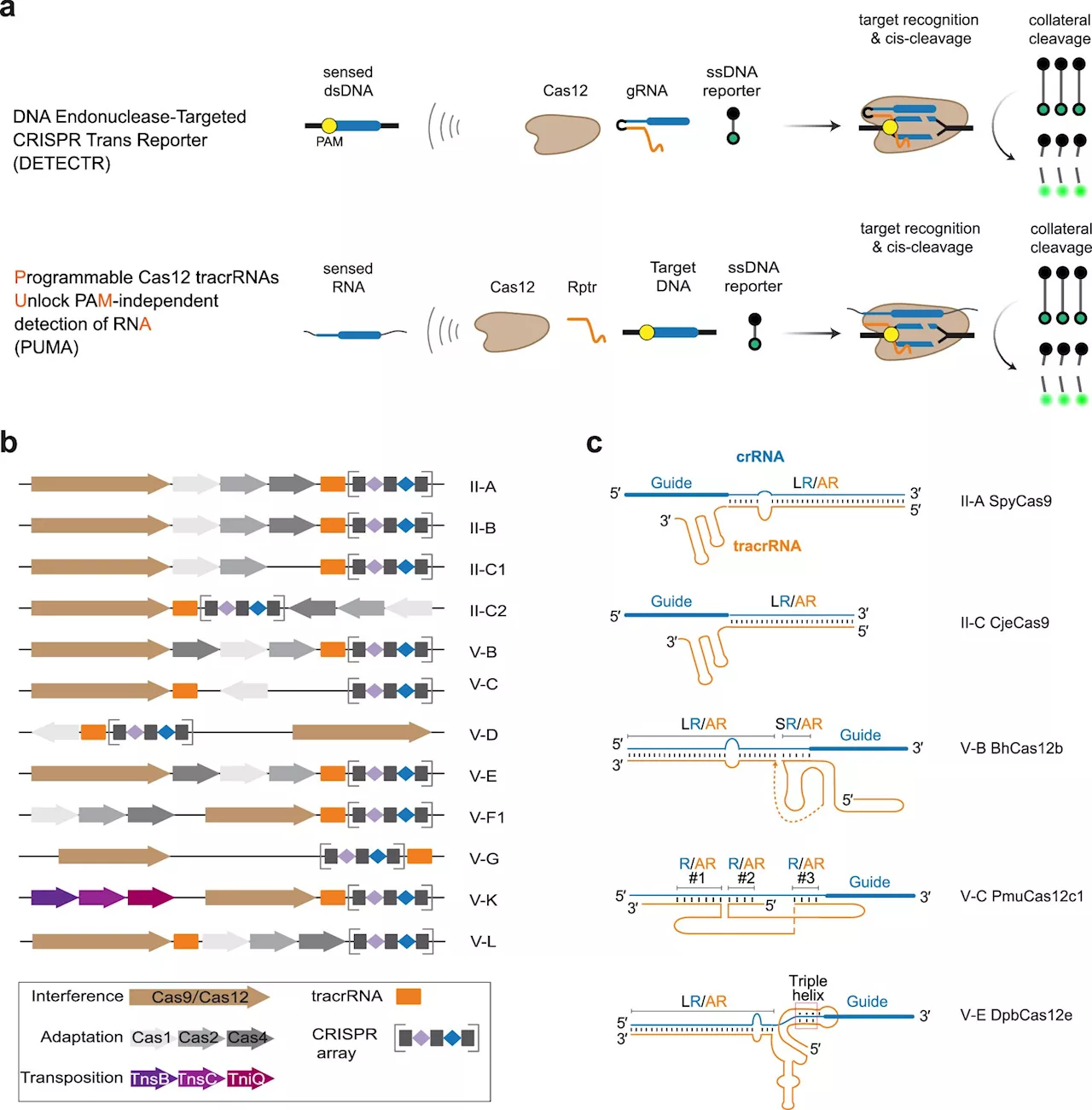 A new addition to the CRISPR toolbox: Teaching the gene scissors to detect RNACRISPR-Cas systems, defense systems in bacteria, have become a plentiful source of technologies for molecular diagnostics. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) in Würzburg have expanded this extensive toolbox.
A new addition to the CRISPR toolbox: Teaching the gene scissors to detect RNACRISPR-Cas systems, defense systems in bacteria, have become a plentiful source of technologies for molecular diagnostics. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) in Würzburg have expanded this extensive toolbox.
Lire la suite »
 A new addition to the CRISPR toolbox: Teaching the gene scissors to detect RNACRISPR-Cas systems, defense systems in bacteria, have become a plentiful source of technologies for molecular diagnostics. Researchers have now expanded this extensive toolbox further. Their novel method, called PUMA, enables the detection of RNA with Cas12 nucleases, which naturally target DNA.
A new addition to the CRISPR toolbox: Teaching the gene scissors to detect RNACRISPR-Cas systems, defense systems in bacteria, have become a plentiful source of technologies for molecular diagnostics. Researchers have now expanded this extensive toolbox further. Their novel method, called PUMA, enables the detection of RNA with Cas12 nucleases, which naturally target DNA.
Lire la suite »
 Modified Self-Amplifying RNA Provides Opportunities For New Vaccines And TreatmentsI am an infectious disease physician, scientist, retired Army colonel, and author of Inside the Hot Zone, a suspenseful account of infectious disease and outbreak crises I managed at the US Army's 'hot zone' lab at Fort Detrick, Maryland.
Modified Self-Amplifying RNA Provides Opportunities For New Vaccines And TreatmentsI am an infectious disease physician, scientist, retired Army colonel, and author of Inside the Hot Zone, a suspenseful account of infectious disease and outbreak crises I managed at the US Army's 'hot zone' lab at Fort Detrick, Maryland.
Lire la suite »
 Bone analysis sheds new light on mysterious species of ancient humanLittle is known about the Denisovans. But a new study is revealing how these enigmatic ancient humans survived in the Tibetan plateau, one of Earth’s most extreme environments.
Bone analysis sheds new light on mysterious species of ancient humanLittle is known about the Denisovans. But a new study is revealing how these enigmatic ancient humans survived in the Tibetan plateau, one of Earth’s most extreme environments.
Lire la suite »
 Legendary Trader Peter Brandt Issues Crucial Bitcoin Warning for BullsPeter Brandt hints at prolonged pain with new Bitcoin price outlook as market sheds $176 billion
Legendary Trader Peter Brandt Issues Crucial Bitcoin Warning for BullsPeter Brandt hints at prolonged pain with new Bitcoin price outlook as market sheds $176 billion
Lire la suite »
