Researchers inoculated oilseed rape plants with a species of fungus that is known for its ability to combat pest insects. Utilizing the relationship between beneficial fungi and crop plants may introduce a new era of agriculture where the plant resilience is improved and the ecological footprint of traditional/chemical pesticides is minimized.
The researchers used Beauveria bassiana, a species of fungus known for its ability to combat pest insects. It is commonly used as a biopesticide that is sprayed on the leaves of crops. These biopesticides are used around the world, but their weakness has been their vulnerability to UV degradation. This led the researchers to explore an alternative approach where they inoculated oilseed rape plants with the fungus to foster a unique symbiotic relationship.
. This way, we aimed to create a natural defense mechanism against pests," explains the first author of the study, Docent Anne Muola from the Biodiversity Unit of the University of Turku.Researchers made a breakthrough by establishing an endophytic relationship between the fungus and oilseed plants. The growth of the fungus in the plant tissue triggered a remarkable increase in flavonoid biosynthesis and compounds known for multiple plant benefits including antioxidant properties.
Flavonoids produced by the oilseed rape plant and renowned for their antioxidant properties and their role in UV protection, flower pigmentation, and herbivore deterrence, took center stage in the study's results. Next, the researchers aim to find out how great of an impact this particularUsing microbes in agriculture can reduce reliance on chemical pesticides
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Unexpected Findings: Researchers Uncover Connection Between Human Genome Topography and Cancer MutationsScientists from the University of California San Diego have discovered a link between the topography of the human genome and the presence of mutations in human cancer. They found that certain regions of the genome, which exhibit unique features, act as hotspots for the accumulation of mutations.
Unexpected Findings: Researchers Uncover Connection Between Human Genome Topography and Cancer MutationsScientists from the University of California San Diego have discovered a link between the topography of the human genome and the presence of mutations in human cancer. They found that certain regions of the genome, which exhibit unique features, act as hotspots for the accumulation of mutations.
Lire la suite »
 Researchers invented a ‘solar leaf’ that harvests 13% more energy from the SunResearchers have created a bio-inspired, hybrid 'solar leaf' that mimics the functions of a leaf to harvest more energy from the Sun.
Researchers invented a ‘solar leaf’ that harvests 13% more energy from the SunResearchers have created a bio-inspired, hybrid 'solar leaf' that mimics the functions of a leaf to harvest more energy from the Sun.
Lire la suite »
 CHLA researchers look to stem cells to repair insulin loss in kids, potential cure for diabetesIn a patient with Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not make insulin because their immune system attacks the islet cells, the cells that make insulin. CHLA researchers are working on ways to replace those cells.
CHLA researchers look to stem cells to repair insulin loss in kids, potential cure for diabetesIn a patient with Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not make insulin because their immune system attacks the islet cells, the cells that make insulin. CHLA researchers are working on ways to replace those cells.
Lire la suite »
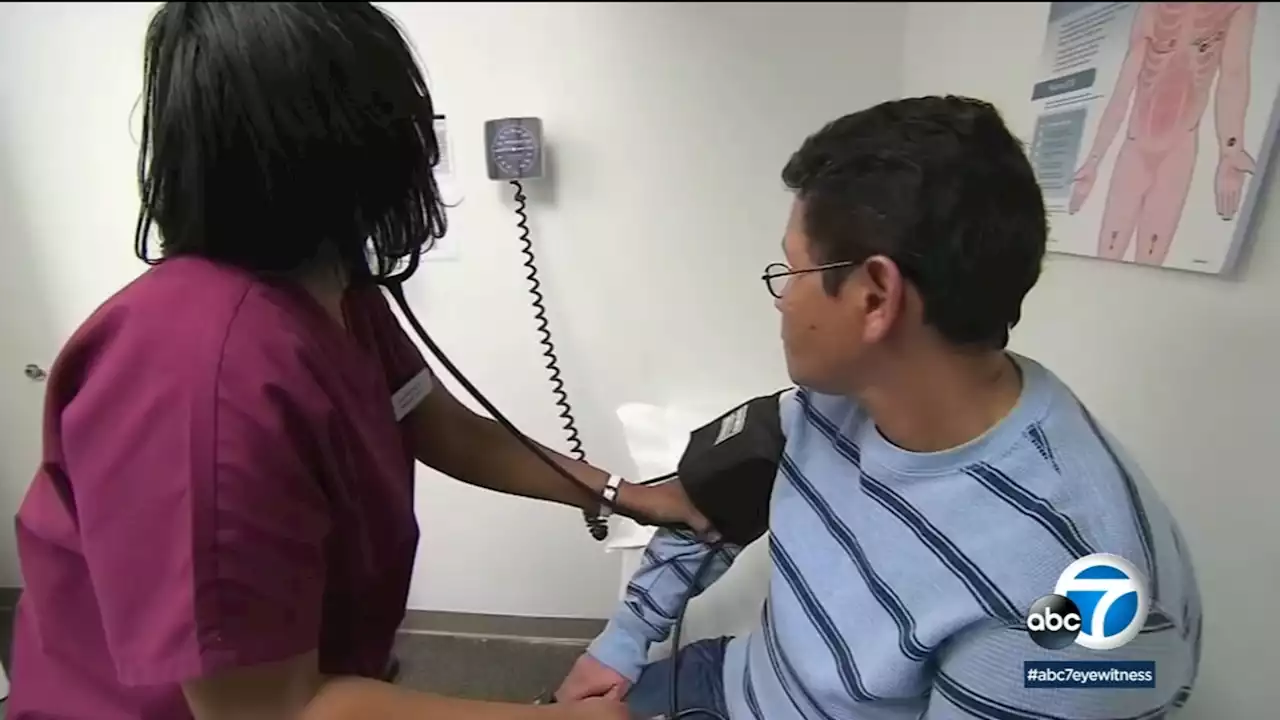 Natural ways to lower high blood pressure might be better than medicine, researchers sayA blood pressure reading of 130 over 80 or more is considered high and if not controlled, it can lead to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. However, there are natural ways you can lower your blood pressure without medications.
Natural ways to lower high blood pressure might be better than medicine, researchers sayA blood pressure reading of 130 over 80 or more is considered high and if not controlled, it can lead to an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. However, there are natural ways you can lower your blood pressure without medications.
Lire la suite »
 Researchers propose using pulsars to localize gravitational wave sourcesCurrent gravitational wave observatories have two significant limitations. The first is that they can only observe powerful gravitational bursts such as the mergers of black holes and neutron stars. The second is that they can only observe these mergers for wavelengths on the order of hundreds to thousands of kilometers. This means we can only observe stellar mass mergers. Of course, there's a lot of interesting gravitational astronomy going on at other wavelengths and noise levels, which has motivated astronomers to get clever. One of these clever ideas is to use pulsars as a telescope. Research has been published on the pre-print server arXiv.
Researchers propose using pulsars to localize gravitational wave sourcesCurrent gravitational wave observatories have two significant limitations. The first is that they can only observe powerful gravitational bursts such as the mergers of black holes and neutron stars. The second is that they can only observe these mergers for wavelengths on the order of hundreds to thousands of kilometers. This means we can only observe stellar mass mergers. Of course, there's a lot of interesting gravitational astronomy going on at other wavelengths and noise levels, which has motivated astronomers to get clever. One of these clever ideas is to use pulsars as a telescope. Research has been published on the pre-print server arXiv.
Lire la suite »
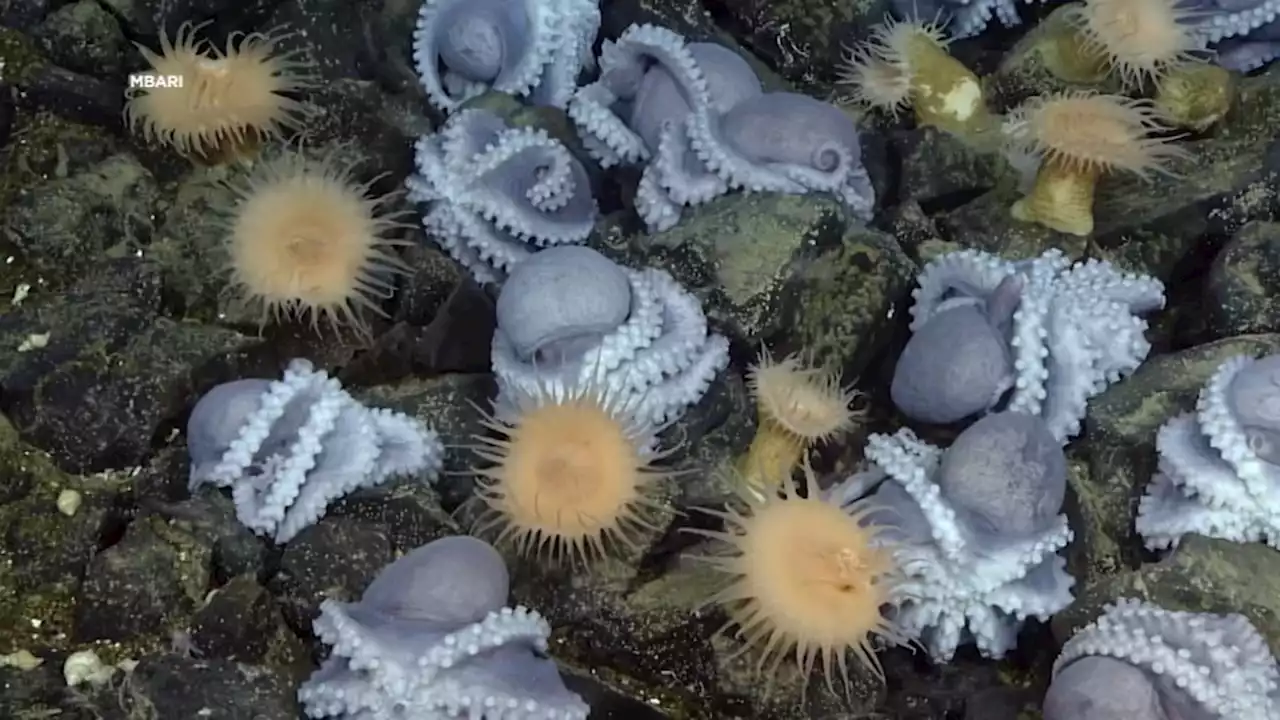 Researchers use underwater technology in Bay Area to unlock mysteries of rare octopus gardenThousands of octopus moms are protecting their newly laid eggs on the ocean floor of the Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary.
Researchers use underwater technology in Bay Area to unlock mysteries of rare octopus gardenThousands of octopus moms are protecting their newly laid eggs on the ocean floor of the Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary.
Lire la suite »
