Exploring long- and short-term mortalities among COVID-19 patients medrxivpreprint Cornell WCMQatar SARSCoV2 COVID19 Mortality
By Bhavana KunkalikarFeb 2 2023Reviewed by Aimee Molineux In a recent study posted to the medRxiv* preprint server, researchers assessed the longer- and short-term all-cause mortalities among severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 -infected patients.
The team assessed the national mortality database along with the national datasets for COVID-19 laboratory testing, immunization, and mortality, which were retrieved via the national platform for digital-health information. A retrospective matched cohort research was performed to explore the incidence of all-cause death noted between a nationwide cohort of individuals with verified primary SARS-CoV-2 infection and a national reference control group including SARS-CoV-2-naive individuals.
Results Each matched cohort comprised 6,85,871 individuals. In the analysis of acute COVID-19 mortality, the median follow-up duration was 91 days. In the primary-infection group, 342 deaths were observed during follow-up, while 288 deaths were noted in the infection-naive group. Among the 342 mortalities, 223 deaths were caused by COVID-19.
During the post-acute period, the aHR comparing mortality incidence in the unvaccinated primary-infection group to the unvaccinated infection-naive group was 0.50. Between the third and seventh month following the main infection, the aHR was 0.41, which rose to 0.76 in the following months. Those who were more clinically susceptible to severe COVID-19 had an aHR of 0.37 during the post-acute phase, while those who were less clinically susceptible to severe COVID-19 had an aHR of 0.77.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 What is the incidence of COVID-19-associated febrile seizures in children?What is the incidence of COVID-19-associated febrile seizures in children? JCM_MDPI COVID19 coronavirus covid febrileseizure seizures pediatrics
What is the incidence of COVID-19-associated febrile seizures in children?What is the incidence of COVID-19-associated febrile seizures in children? JCM_MDPI COVID19 coronavirus covid febrileseizure seizures pediatrics
Lire la suite »
 COVID-19 might increase risk of autoimmune diseasesCOVID-19 might increase risk of autoimmune diseases medrxivpreprint Medizin_TUD COVID19 SARSCoV2 AutoimmuneDiseases
COVID-19 might increase risk of autoimmune diseasesCOVID-19 might increase risk of autoimmune diseases medrxivpreprint Medizin_TUD COVID19 SARSCoV2 AutoimmuneDiseases
Lire la suite »
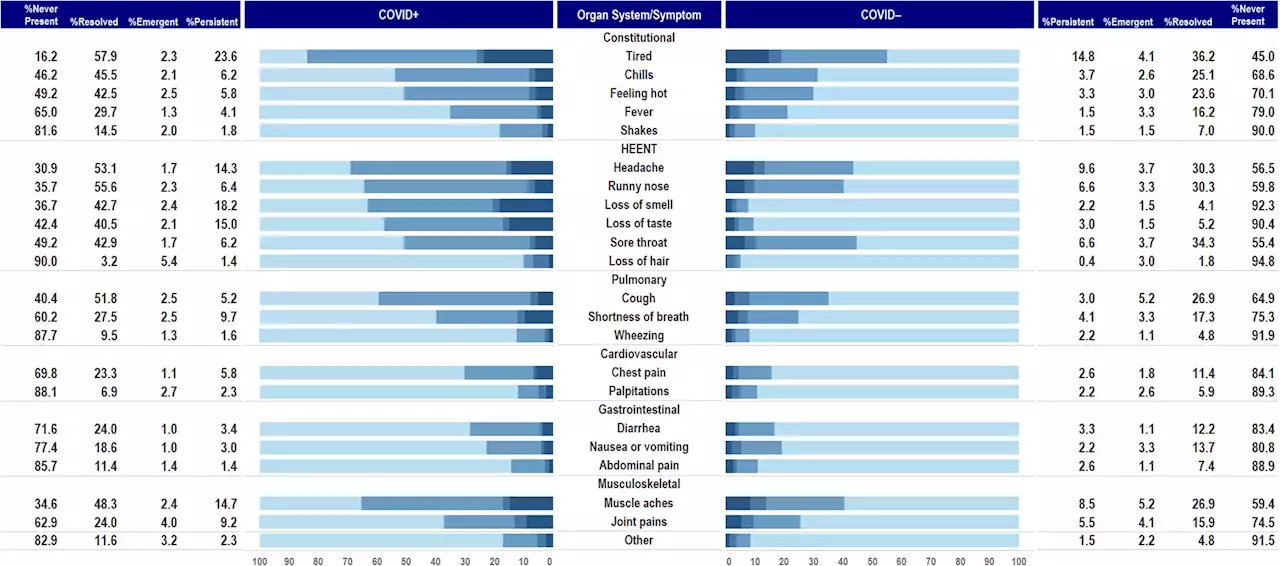 Study shows persistent symptoms are common three months after testing for COVID-19In a new study from INSPIRE (Innovative Support for Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infections Registry), researchers compared new and ongoing symptoms and outcomes in both COVID-positive and COVID-negative adults who were tested because of acute COVID-19-like symptoms. The study found that half of the patients with COVID-19 and one-quarter of those who tested negative had at least one symptom at three months follow-up.
Study shows persistent symptoms are common three months after testing for COVID-19In a new study from INSPIRE (Innovative Support for Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infections Registry), researchers compared new and ongoing symptoms and outcomes in both COVID-positive and COVID-negative adults who were tested because of acute COVID-19-like symptoms. The study found that half of the patients with COVID-19 and one-quarter of those who tested negative had at least one symptom at three months follow-up.
Lire la suite »
 A wave of films and television shows is exploring psychotherapy“Couples Therapy” and “Stutz” profess to be educational. But, even in this format, professional boundaries are muddled; confidentiality is obliterated
A wave of films and television shows is exploring psychotherapy“Couples Therapy” and “Stutz” profess to be educational. But, even in this format, professional boundaries are muddled; confidentiality is obliterated
Lire la suite »
 Researchers find a way to make VR headsets more realisticA group of researchers have come up with a way of arranging LED pixels to produce screens with a much higher resolution than is currently possible. This could be used to make VR images more lifelike
Researchers find a way to make VR headsets more realisticA group of researchers have come up with a way of arranging LED pixels to produce screens with a much higher resolution than is currently possible. This could be used to make VR images more lifelike
Lire la suite »
 Researchers report a heterologous vaccination strategy against IBV in ChickensResearchers reported on the immunogenicity of a heterologous vaccine regimen against IBV, comprising prime doses of QAC-encapsulated plasmid and a booster dose of MVA.
Researchers report a heterologous vaccination strategy against IBV in ChickensResearchers reported on the immunogenicity of a heterologous vaccine regimen against IBV, comprising prime doses of QAC-encapsulated plasmid and a booster dose of MVA.
Lire la suite »
