Using organ-on-a-chiptechnology to elucidate the liver pathophysiology of COVID-19patients PNASNexus
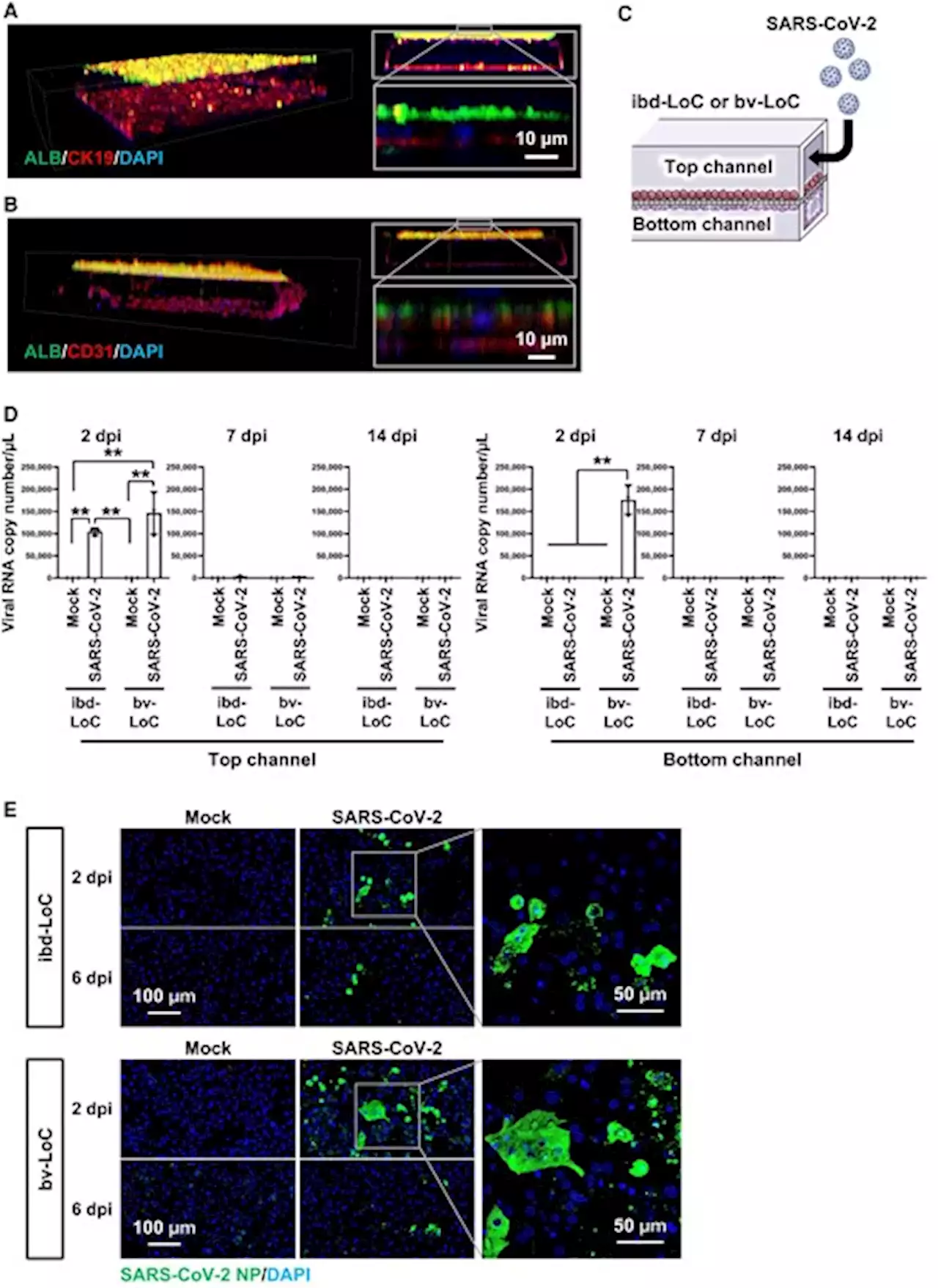
B). On the other hand, the probabilities of abnormal ALP and T-BIL in mild and severe COVID-19 patients were similar to each other. These results suggest that hepatic dysfunction but not hepatobiliary disease was induced in severe COVID-19 patients. The findings from the clinical samples analysis are consistent with the phenomena observed in our in vitro data.Comparison of the results obtained from LoCs and clinical data of COVID-19 patients.
In SARS-CoV-2-infected bv-LoCs, endothelial barrier function was decreased. Such endothelial barrier disruption was also reported in SARS-CoV-2-infected airway-, lung- and gut-on-a-chip (
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Organ and cell-specific biomarkers of Long-COVID identified with targeted proteomics and machine learning - Molecular MedicineBackground Survivors of acute COVID-19 often suffer prolonged, diffuse symptoms post-infection, referred to as “Long-COVID”. A lack of Long-COVID biomarkers and pathophysiological mechanisms limits effective diagnosis, treatment and disease surveillance. We performed targeted proteomics and machine learning analyses to identify novel blood biomarkers of Long-COVID. Methods A case–control study comparing the expression of 2925 unique blood proteins in Long-COVID outpatients versus COVID-19 inpatients and healthy control subjects. Targeted proteomics was accomplished with proximity extension assays, and machine learning was used to identify the most important proteins for identifying Long-COVID patients. Organ system and cell type expression patterns were identified with Natural Language Processing (NLP) of the UniProt Knowledgebase. Results Machine learning analysis identified 119 relevant proteins for differentiating Long-COVID outpatients (Bonferonni corrected P | 0.01). Protein combinations were narrowed down to two optimal models, with nine and five proteins each, and with both having excellent sensitivity and specificity for Long-COVID status (AUC = 1.00, F1 = 1.00). NLP expression analysis highlighted the diffuse organ system involvement in Long-COVID, as well as the involved cell types, including leukocytes and platelets, as key components associated with Long-COVID. Conclusions Proteomic analysis of plasma from Long-COVID patients identified 119 highly relevant proteins and two optimal models with nine and five proteins, respectively. The identified proteins reflected widespread organ and cell type expression. Optimal protein models, as well as individual proteins, hold the potential for accurate diagnosis of Long-COVID and targeted therapeutics.
Organ and cell-specific biomarkers of Long-COVID identified with targeted proteomics and machine learning - Molecular MedicineBackground Survivors of acute COVID-19 often suffer prolonged, diffuse symptoms post-infection, referred to as “Long-COVID”. A lack of Long-COVID biomarkers and pathophysiological mechanisms limits effective diagnosis, treatment and disease surveillance. We performed targeted proteomics and machine learning analyses to identify novel blood biomarkers of Long-COVID. Methods A case–control study comparing the expression of 2925 unique blood proteins in Long-COVID outpatients versus COVID-19 inpatients and healthy control subjects. Targeted proteomics was accomplished with proximity extension assays, and machine learning was used to identify the most important proteins for identifying Long-COVID patients. Organ system and cell type expression patterns were identified with Natural Language Processing (NLP) of the UniProt Knowledgebase. Results Machine learning analysis identified 119 relevant proteins for differentiating Long-COVID outpatients (Bonferonni corrected P | 0.01). Protein combinations were narrowed down to two optimal models, with nine and five proteins each, and with both having excellent sensitivity and specificity for Long-COVID status (AUC = 1.00, F1 = 1.00). NLP expression analysis highlighted the diffuse organ system involvement in Long-COVID, as well as the involved cell types, including leukocytes and platelets, as key components associated with Long-COVID. Conclusions Proteomic analysis of plasma from Long-COVID patients identified 119 highly relevant proteins and two optimal models with nine and five proteins, respectively. The identified proteins reflected widespread organ and cell type expression. Optimal protein models, as well as individual proteins, hold the potential for accurate diagnosis of Long-COVID and targeted therapeutics.
Lire la suite »
 Autoantibodies against chemokines post-SARS-CoV-2 infection correlate with disease course - Nature ImmunologyRobbiani and colleagues show that antibodies against specific chemokines are detected in COVID-19 convalescents and may modulate the inflammatory response and disease outcome.
Autoantibodies against chemokines post-SARS-CoV-2 infection correlate with disease course - Nature ImmunologyRobbiani and colleagues show that antibodies against specific chemokines are detected in COVID-19 convalescents and may modulate the inflammatory response and disease outcome.
Lire la suite »
 SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Dynamics in Healthcare Workers after mRNA VaccinationSince the emergence of SARS-CoV-2, maintaining healthcare worker (HCW) health and safety has been fundamental to responding to the global pandemic. Vaccination with mRNA-base vaccines targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein has emerged as a key strategy in reducing HCW susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, however, neutralizing antibody responses subside with time and may be influenced by many variables. We sought to understand the dynamics between vaccine products, prior clinical illness from SARS-CoV-2, and incidence of vaccine-associated adverse reactions on antibody decay over time in HCWs at a university medical center. A cohort of 296 HCWs received standard two-dose vaccination with either bnt162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) or mRNA-1273 (Moderna) and were evaluated after two, six, and nine months. Subjects were grouped by antibody decay curve into steep antibody decliners gentle decliners. Vaccination with mRNA-1273 led to more sustained antibody responses compared to bnt162b2. Subjects experiencing vaccine-associated symptoms were more likely to experience a more prolonged neutralizing antibody response. Subjects with clinical SARS-CoV-2 infection prior to vaccination were more likely to experience vaccination-associated symptoms after first vaccination and were more likely to have a more blunted antibody decay. Understanding factors associated with vaccine efficacy may assist clinicians in determining appropriate vaccine strategies in HCWs.
SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Dynamics in Healthcare Workers after mRNA VaccinationSince the emergence of SARS-CoV-2, maintaining healthcare worker (HCW) health and safety has been fundamental to responding to the global pandemic. Vaccination with mRNA-base vaccines targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein has emerged as a key strategy in reducing HCW susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, however, neutralizing antibody responses subside with time and may be influenced by many variables. We sought to understand the dynamics between vaccine products, prior clinical illness from SARS-CoV-2, and incidence of vaccine-associated adverse reactions on antibody decay over time in HCWs at a university medical center. A cohort of 296 HCWs received standard two-dose vaccination with either bnt162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) or mRNA-1273 (Moderna) and were evaluated after two, six, and nine months. Subjects were grouped by antibody decay curve into steep antibody decliners gentle decliners. Vaccination with mRNA-1273 led to more sustained antibody responses compared to bnt162b2. Subjects experiencing vaccine-associated symptoms were more likely to experience a more prolonged neutralizing antibody response. Subjects with clinical SARS-CoV-2 infection prior to vaccination were more likely to experience vaccination-associated symptoms after first vaccination and were more likely to have a more blunted antibody decay. Understanding factors associated with vaccine efficacy may assist clinicians in determining appropriate vaccine strategies in HCWs.
Lire la suite »
 How SARS-CoV-2 infection affects acute ischemic stroke outcomesHow SARS-CoV-2 infection affects acute ischemic stroke outcomes IschemicStroke SARSCoV2 Stroke Coronavirus Disease COVID Pneumonia Cardiovascular Reperfusion CreactiveProtein PLOSONE semmelweishu
How SARS-CoV-2 infection affects acute ischemic stroke outcomesHow SARS-CoV-2 infection affects acute ischemic stroke outcomes IschemicStroke SARSCoV2 Stroke Coronavirus Disease COVID Pneumonia Cardiovascular Reperfusion CreactiveProtein PLOSONE semmelweishu
Lire la suite »
 Zoo study: SARS-CoV-2 surveillance across all mammal speciesZoo study: SARS-CoV-2 surveillance across all mammal species Zoology Coronavirus Disease COVID SARSCoV2 AntwerpZoo PlanckendaelZoo biorxivpreprint UAntwerpen belgiannatural RBSZ3
Zoo study: SARS-CoV-2 surveillance across all mammal speciesZoo study: SARS-CoV-2 surveillance across all mammal species Zoology Coronavirus Disease COVID SARSCoV2 AntwerpZoo PlanckendaelZoo biorxivpreprint UAntwerpen belgiannatural RBSZ3
Lire la suite »
 The effect of variation of individual infectiousness on SARS-CoV-2 transmission in householdsHousehold transmission modeling qualified variation of individual infectiousness among infected persons, which could be caused by both biological factors and host behaviors.
The effect of variation of individual infectiousness on SARS-CoV-2 transmission in householdsHousehold transmission modeling qualified variation of individual infectiousness among infected persons, which could be caused by both biological factors and host behaviors.
Lire la suite »