New Hope to Find Life on Enceladus After Scientists Detect Phosphorus
Saturn, and by extension, Enceladus, are far from the life-nurturing warmth of the Sun, on which the vast majority of Earth's food webs rely. But here on Earth, in the very dark, cold regions of the deep sea, where the Sun's rays don't penetrate, food webs that rely on chemistry thrive around heat vents in the ocean floor.
Such might also be the case for Enceladus, but it's not like we can just nip on over and send a submarine below the at leastLuckily, Enceladus is a messy wee beastie. Those geysers are an active, ongoing feature; in fact, they create and maintain Saturn's second-outermost E ring, a fuzzy torus of material that's mostly microscopic particles of water ice, in which Enceladus is cozily ensconced., sampled that ring, collecting the light shimmering off the ice.
Postberg and his colleagues did this, taking data from Cassini's Cosmic Dust Analyzer instrument and conducting a comprehensive analysis of 345 particles. On nine of those particles, they identified spectral features they found to be unique to sodium phosphate – a compound of sodium and phosphorus. Next, they conducted an experiment to try and replicate the spectrum, firing a laser at a beam of water in which sodium orthophosphate and disodium hydrogen phosphate had been dissolved. They were able to reproduce the chemical fingerprint they found in the ice grains of the E ring. And the abundance of these elements required to reproduce the spectrum suggests a high abundance of sodium in Enceladus's ocean.
."Even with a conservative margin, our estimate indicates concentrations in the order of at least hundreds of micromolar, several 100-fold the average phosphate abundance in Earth's oceans."of a type of rock called carbonaceous chondritic rock. The team conducted experiments in that direction and found that phosphorus is an unavoidable product of the interaction between alkaline and carbonate-rich ocean water and this rock.
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Scientists Detect Fastest Runaway Star Ever Seen in The Milky WayThe new discovery of six more runaway stars in the Milky Way has landed the fastest object of this type yet detected in the galaxy.
Scientists Detect Fastest Runaway Star Ever Seen in The Milky WayThe new discovery of six more runaway stars in the Milky Way has landed the fastest object of this type yet detected in the galaxy.
Lire la suite »
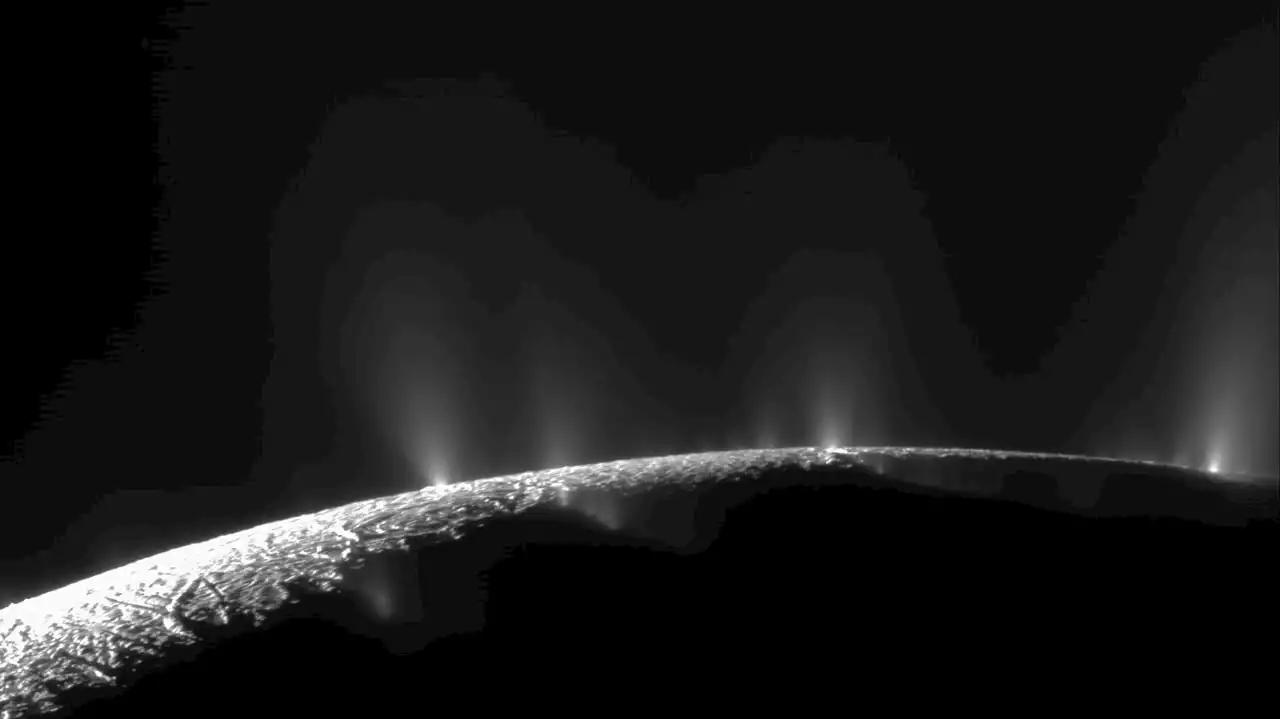 Saturn’s Icy Moon Enceladus Has All the Ingredients Needed to Make Life'Our Cassini-[Cosmic Dust Analyzer] measurements leave no doubt that substantial quantities of this essential substance are present in the ocean water,' Frank Postberg, a planetary scientist at Freie Universitat Berlin who led the new study, said.
Saturn’s Icy Moon Enceladus Has All the Ingredients Needed to Make Life'Our Cassini-[Cosmic Dust Analyzer] measurements leave no doubt that substantial quantities of this essential substance are present in the ocean water,' Frank Postberg, a planetary scientist at Freie Universitat Berlin who led the new study, said.
Lire la suite »
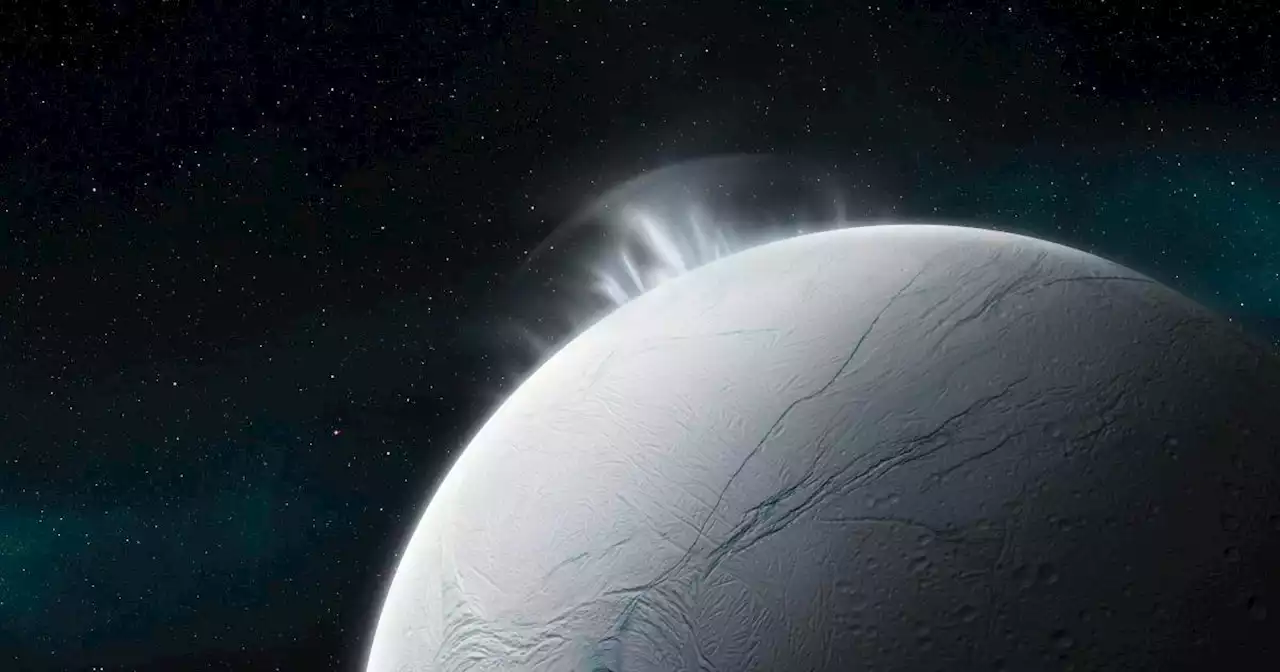 Saturn’s moon Enceladus could support species similar to Earth | EngadgetSaturn’s moon Enceladus could support species similar to Earth
Saturn’s moon Enceladus could support species similar to Earth | EngadgetSaturn’s moon Enceladus could support species similar to Earth
Lire la suite »
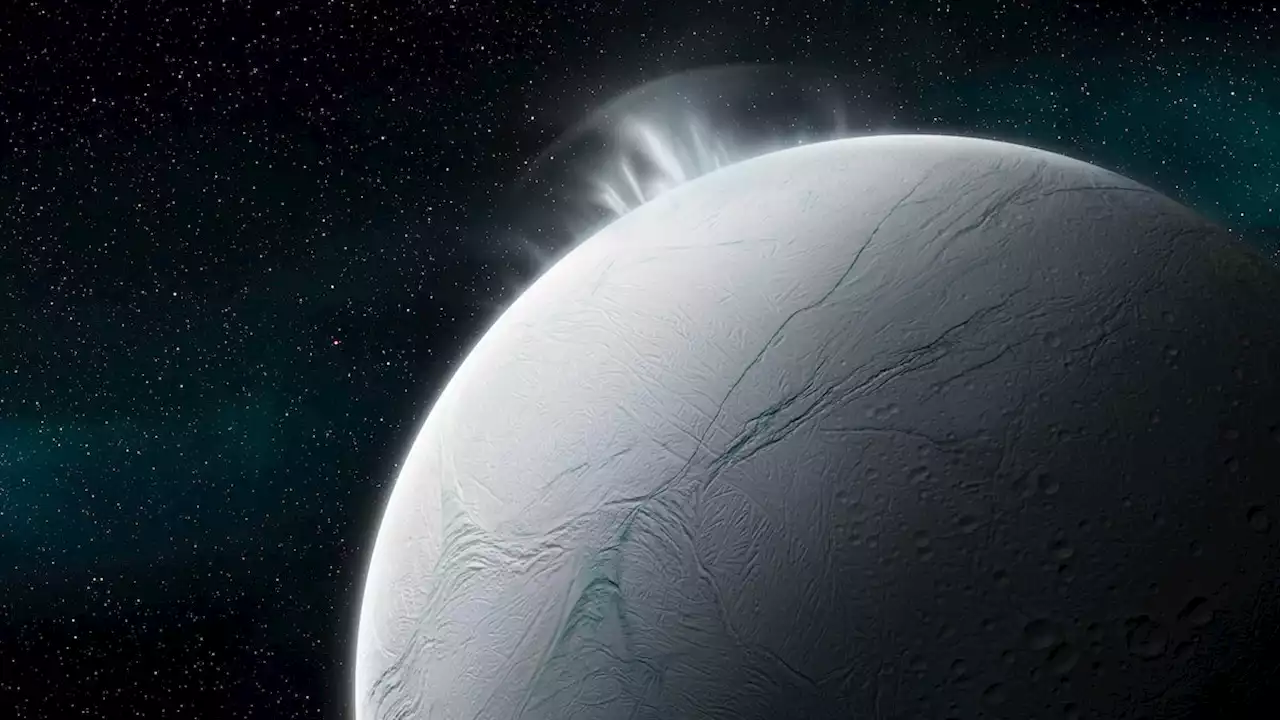 Discovery shows Saturn's moon Enceladus has everything needed for lifeEnceladus is considered one of the most promising places to search for alien life. Now scientists have detected the last of six necessary ingredients: phosphorous.
Discovery shows Saturn's moon Enceladus has everything needed for lifeEnceladus is considered one of the most promising places to search for alien life. Now scientists have detected the last of six necessary ingredients: phosphorous.
Lire la suite »
 An Element Critical for (Earth) Life is Spewing out of EnceladusScientists examining Cassini data find evidence of phosphorus in the icy subsurface ocean in Saturn's moon Enceladus.
An Element Critical for (Earth) Life is Spewing out of EnceladusScientists examining Cassini data find evidence of phosphorus in the icy subsurface ocean in Saturn's moon Enceladus.
Lire la suite »
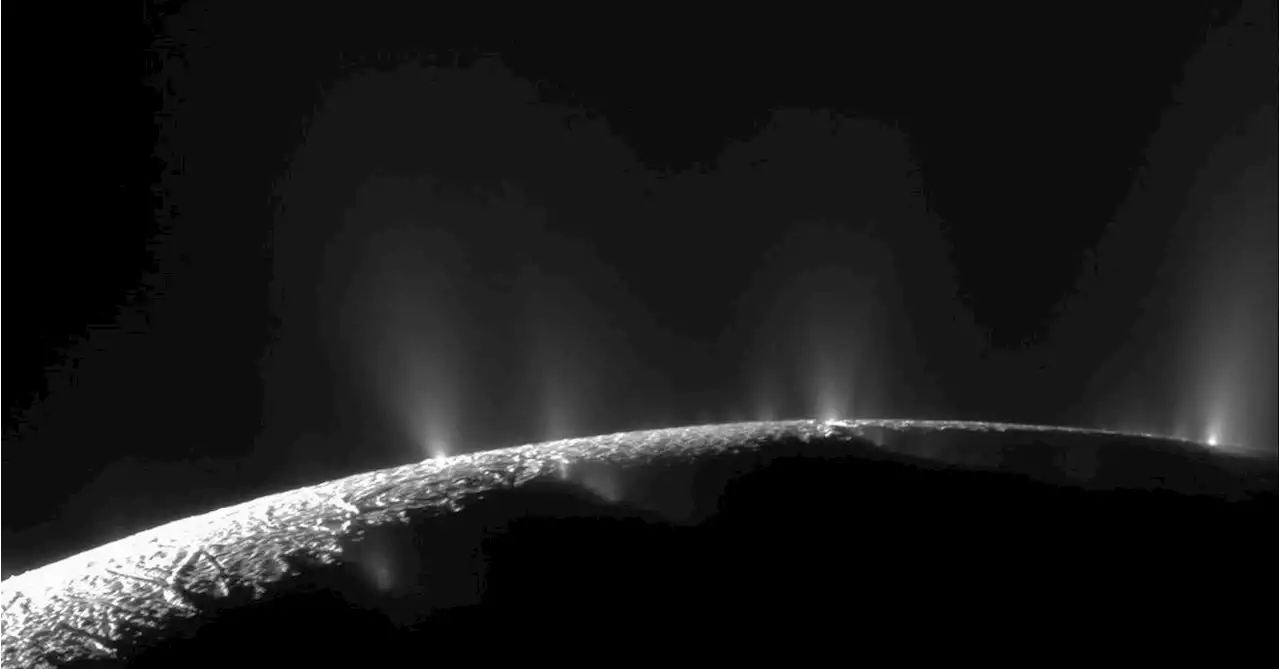 Saturn's icy moon Enceladus harbors essential elements for lifeHigh concentrations of phosphorus, an essential element for all biological processes on Earth, have been detected in ice crystals spewed from the interior ocean of Saturn's moon Enceladus, adding to its potential to harbor life, researchers reported on Wednesday.
Saturn's icy moon Enceladus harbors essential elements for lifeHigh concentrations of phosphorus, an essential element for all biological processes on Earth, have been detected in ice crystals spewed from the interior ocean of Saturn's moon Enceladus, adding to its potential to harbor life, researchers reported on Wednesday.
Lire la suite »
