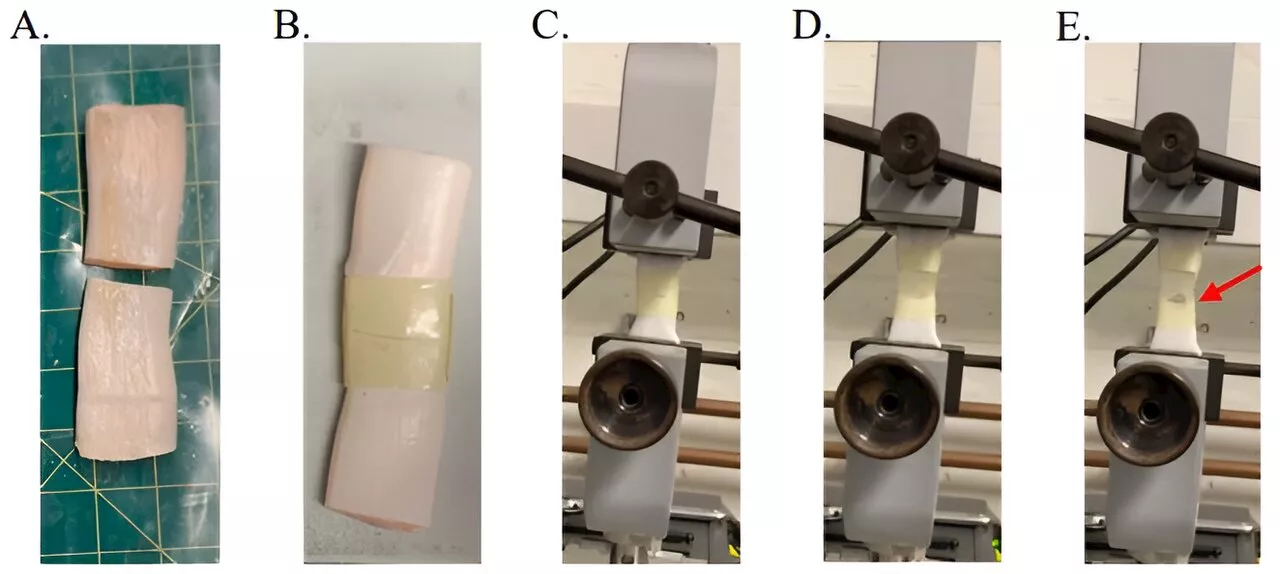
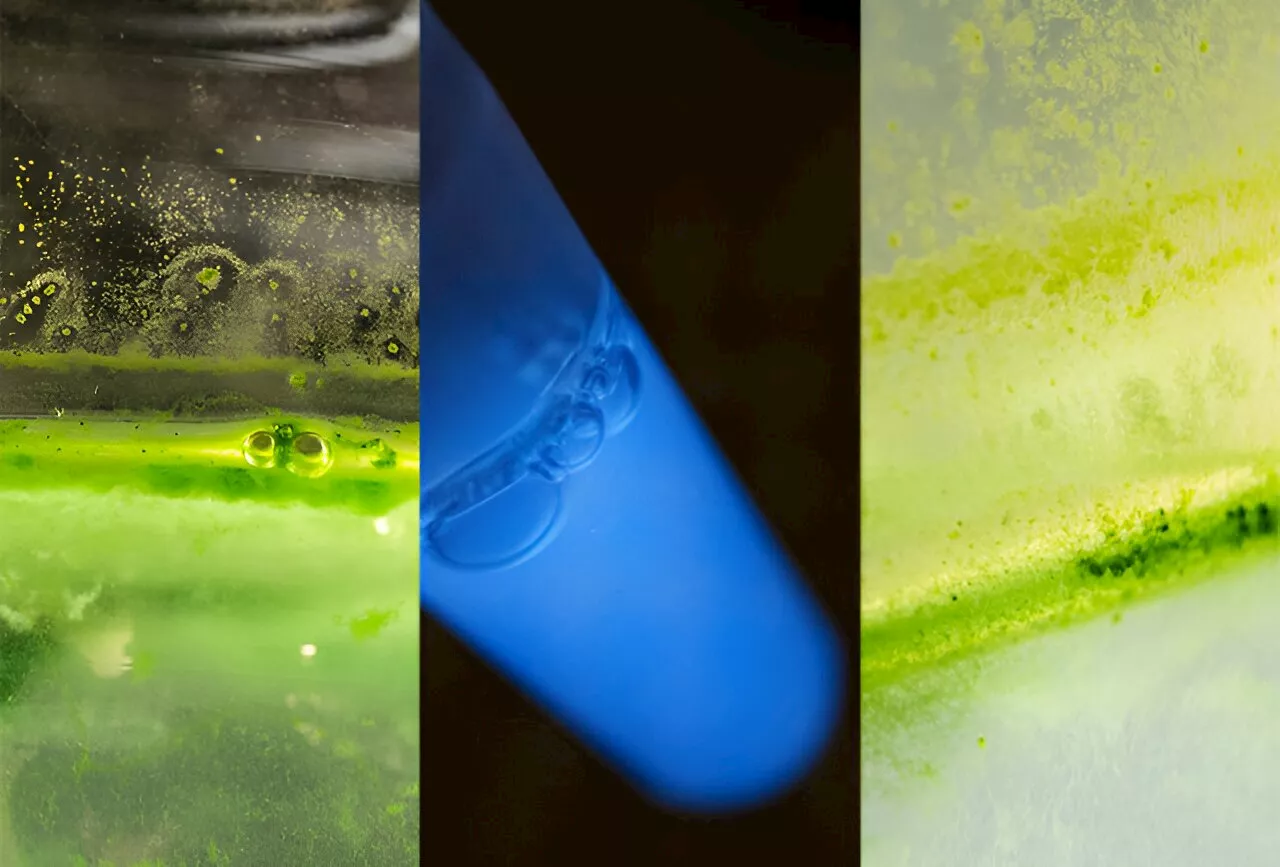
Researchers want to transform the natural and abundant resource wood into useful materials, and central to that is a molecular machine found in fungi that decomposes the complex raw material into its basic components.
Bioengineers create new substrate to study wood-decomposing enzyme retrieved 18 September 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-09-bioengineers-substrate-wood-decomposing-enzyme.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
Physics News Science News Technology News Physics Materials Nanotech Technology Science
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Bioengineers develop a new environmentally friendly adhesive polymerA team of bioengineers at the University of California, Berkeley, has developed a new kind of environmentally friendly adhesive polymer. In their study, published in the journal Science, the group used an electrophilic stabilizer to prevent a certain fatty acid from depolymerizing, thereby enabling its use as an adhesive.
Bioengineers develop a new environmentally friendly adhesive polymerA team of bioengineers at the University of California, Berkeley, has developed a new kind of environmentally friendly adhesive polymer. In their study, published in the journal Science, the group used an electrophilic stabilizer to prevent a certain fatty acid from depolymerizing, thereby enabling its use as an adhesive.
Lire la suite »
 Bioengineers develop lotus leaf-inspired system to advance study of cancer cell clustersBioengineers have harnessed the lotus effect to develop a system for culturing cancer cell clusters that can shed light on hard-to-study tumor properties.
Bioengineers develop lotus leaf-inspired system to advance study of cancer cell clustersBioengineers have harnessed the lotus effect to develop a system for culturing cancer cell clusters that can shed light on hard-to-study tumor properties.
Lire la suite »
 Bioengineers develop protein assembly road map for nature-derived nanobubblesAs far as water gear goes, floaties are not exactly high tech. But the tiny air-filled bubbles some microorganisms use as flotation devices when they compete for light on the water surface are a different story.
Bioengineers develop protein assembly road map for nature-derived nanobubblesAs far as water gear goes, floaties are not exactly high tech. But the tiny air-filled bubbles some microorganisms use as flotation devices when they compete for light on the water surface are a different story.
Lire la suite »
 Researchers give adult zebra finches back their ability to learn new songsWe all know the adage, 'You can't teach an old dog new tricks.' As we age, our ability to learn new skills, like mastering a foreign language or picking up a musical instrument, seems to fade. The culprit? A decline in brain plasticity - the brain's capacity to rewire itself and adapt to new challenges.
Researchers give adult zebra finches back their ability to learn new songsWe all know the adage, 'You can't teach an old dog new tricks.' As we age, our ability to learn new skills, like mastering a foreign language or picking up a musical instrument, seems to fade. The culprit? A decline in brain plasticity - the brain's capacity to rewire itself and adapt to new challenges.
Lire la suite »
 Researchers develop tool that measures health of a person's gut microbiomeA team of researchers has developed an innovative computational tool that analyzes the gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms within the digestive system, to provide insights into overall well-being.
Researchers develop tool that measures health of a person's gut microbiomeA team of researchers has developed an innovative computational tool that analyzes the gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses and other microorganisms within the digestive system, to provide insights into overall well-being.
Lire la suite »
 Researchers explore key interaction sites and pathways in ammonia captureThe design and development of high-performance materials are crucial for efficient ammonia capture. Generally, these materials are characterized by abundant ammonia adsorption sites and rapid ammonia transport channels, enabling the effective capture and release of ammonia molecules.
Researchers explore key interaction sites and pathways in ammonia captureThe design and development of high-performance materials are crucial for efficient ammonia capture. Generally, these materials are characterized by abundant ammonia adsorption sites and rapid ammonia transport channels, enabling the effective capture and release of ammonia molecules.
Lire la suite »
