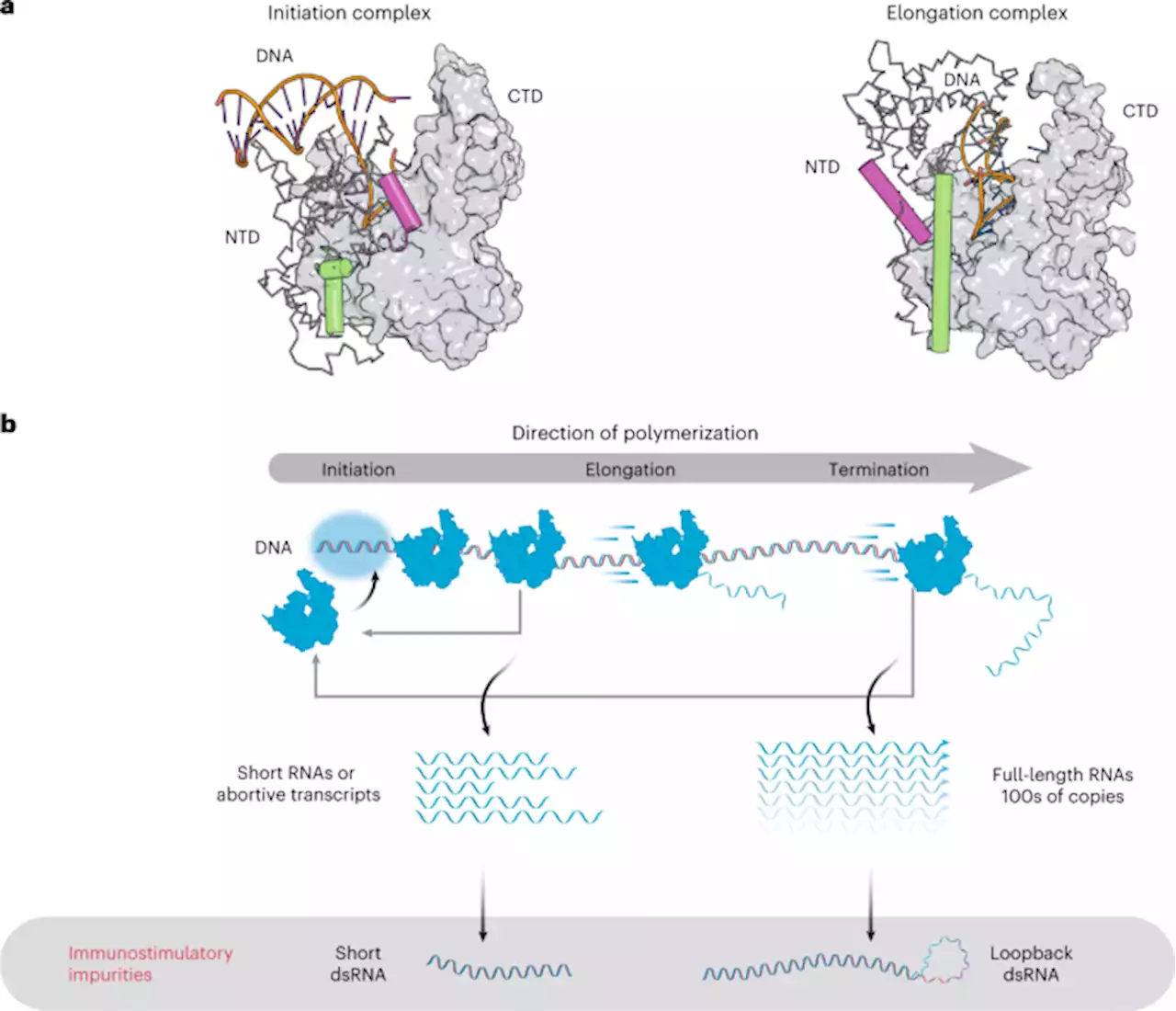
An engineered T7 RNA polymerase that produces mRNA free of immunostimulatory byproducts
pyrophosphatase and 1.8 µM dsDNA template in 1× IVT buffer . The dsDNA template was generated by annealing synthetic DNA sequences containing the T7 promoter in 1× phosphate-buffered saline . This template has a G-rich initiation sequence of 42 nucleotides, enhancing T7 RNAP EC transition, before the first incorporation of CTP at position 43.
, BJ fibroblasts acquired from the American Type Culture Collection were cultured in complete media comprising Eagle’s minimal essential medium with-glutamine supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum . Cells were seeded in 96-well cell culture plates at 20,000 cells per well and maintained for 24 h before transfection. Cells were transfected with mRNA or poly using Lipofectamine 2000 .
France Dernières Nouvelles, France Actualités
Similar News:Vous pouvez également lire des articles d'actualité similaires à celui-ci que nous avons collectés auprès d'autres sources d'information.
 Probing the dynamic RNA structurome and its functions - Nature Reviews GeneticsIn this Review, Spitale and Incarnato discuss how the application of sequencing-based RNA structure mapping methods to entire transcriptomes in living cells is providing insight into the RNA structurome, the dynamics of RNA ensembles and how RNA structure regulates cellular processes.
Probing the dynamic RNA structurome and its functions - Nature Reviews GeneticsIn this Review, Spitale and Incarnato discuss how the application of sequencing-based RNA structure mapping methods to entire transcriptomes in living cells is providing insight into the RNA structurome, the dynamics of RNA ensembles and how RNA structure regulates cellular processes.
Lire la suite »
 Nature Biotechnology - Protein structure predictionThe November issue is live On our cover, Chowdhury et al. present a deep learning method to predict a protein’s structure from its sequence alone, with applications to orphan and de novo–designed proteins
Nature Biotechnology - Protein structure predictionThe November issue is live On our cover, Chowdhury et al. present a deep learning method to predict a protein’s structure from its sequence alone, with applications to orphan and de novo–designed proteins
Lire la suite »
 Spatial genomics maps the structure, nature and evolution of cancer clones - NatureA workflow centred around base-specific in situ sequencing generates detailed maps of, and can phenotypically characterize, the unique set of subclones of cancers.
Spatial genomics maps the structure, nature and evolution of cancer clones - NatureA workflow centred around base-specific in situ sequencing generates detailed maps of, and can phenotypically characterize, the unique set of subclones of cancers.
Lire la suite »
 Frontiers | The epitranscriptome of Vero cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 assessed by direct RNA sequencing reveals m6A pattern changes and DRACH motif biases in viral and cellular RNAsThe epitranscriptomics of the SARS-CoV-2 infected cell reveals its response to viral replication. Among various types of RNA nucleotide modifications, the m6A is the most common and is involved in several crucial processes of RNA intracellular location, maturation, half-life and translatability. This epitranscriptome contains a mixture of viral RNAs and cellular transcripts. In a previous study we presented the analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA m6A methylation based on direct RNA sequencing and characterized DRACH motif mutations in different viral lineages. Here we present the analysis of the m6A transcript methylation of Vero cells (derived from African Green Monkeys) and Calu-3 cells (human) upon infection by SARS-CoV-2 using direct RNA sequencing data. Analysis of these data by nonparametric statistics and two computational methods (m6anet and EpiNano) show that m6A levels are higher in RNAs of infected cells. Functional enrichment analysis reveals increased m6A methylation of transcripts involved in translation, peptide and amine metabolism. This analysis allowed the identification of differentially methylated transcripts and m6A unique sites in the infected cell transcripts. Results here presented indicate that the cell response to viral infection not only changes the levels of mRNAs, as previously shown, but also its epitranscriptional pattern. Also, transcriptome-wide analysis shows strong nucleotide biases in DRACH motifs of cellular transcripts, both in Vero and Calu-3 cells, which use the signature GGACU whereas in viral RNAs the signature is GAACU. We hypothesize that the differences of DRACH motif biases, might force the convergent evolution of the viral genome resulting in better adaptation to target sequence preferences of writer, reader and eraser enzymes. To our knowledge, this is the first report on m6A epitranscriptome of the SARS-CoV-2 infected Vero cells by direct RNA sequencing, which is the sensu stricto RNA-seq.
Frontiers | The epitranscriptome of Vero cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 assessed by direct RNA sequencing reveals m6A pattern changes and DRACH motif biases in viral and cellular RNAsThe epitranscriptomics of the SARS-CoV-2 infected cell reveals its response to viral replication. Among various types of RNA nucleotide modifications, the m6A is the most common and is involved in several crucial processes of RNA intracellular location, maturation, half-life and translatability. This epitranscriptome contains a mixture of viral RNAs and cellular transcripts. In a previous study we presented the analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA m6A methylation based on direct RNA sequencing and characterized DRACH motif mutations in different viral lineages. Here we present the analysis of the m6A transcript methylation of Vero cells (derived from African Green Monkeys) and Calu-3 cells (human) upon infection by SARS-CoV-2 using direct RNA sequencing data. Analysis of these data by nonparametric statistics and two computational methods (m6anet and EpiNano) show that m6A levels are higher in RNAs of infected cells. Functional enrichment analysis reveals increased m6A methylation of transcripts involved in translation, peptide and amine metabolism. This analysis allowed the identification of differentially methylated transcripts and m6A unique sites in the infected cell transcripts. Results here presented indicate that the cell response to viral infection not only changes the levels of mRNAs, as previously shown, but also its epitranscriptional pattern. Also, transcriptome-wide analysis shows strong nucleotide biases in DRACH motifs of cellular transcripts, both in Vero and Calu-3 cells, which use the signature GGACU whereas in viral RNAs the signature is GAACU. We hypothesize that the differences of DRACH motif biases, might force the convergent evolution of the viral genome resulting in better adaptation to target sequence preferences of writer, reader and eraser enzymes. To our knowledge, this is the first report on m6A epitranscriptome of the SARS-CoV-2 infected Vero cells by direct RNA sequencing, which is the sensu stricto RNA-seq.
Lire la suite »
A new treaty process offers hope to end plastic pollution - Nature Reviews Earth & EnvironmentThe development of a global legally binding treaty by the UN to end plastic pollution is underway. To be effective, the global treaty requires new levels of transparency, disclosure and cooperation to support evidence-based policymaking that avoids the fragmented and reactionary policies of the past.
Lire la suite »
Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir - NatureNature research paper: Multiple pathways for SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir
Lire la suite »